Part 7: The 2020 Wilson Research Group Functional Verification Study
IC/ASIC Design Trends
This blog is a continuation of a series of blogs related to the 2020 Wilson Research Group Functional Verification Study. In my previous blog, I focused on FPGA design and verification trends. Now my plan is to shift the focus in this series of blogs from FPGA trends to IC/ASIC trends. And specifically in this blog, I present trends related to various aspects of design to illustrate growing design complexity.
IC/ASIC Design Size by Gate Count
Figure 7-1 shows the trends from the 2012 through the 2020 studies in terms of active IC/ASIC design project by design sizes (gates of logic and datapath, excluding memories). Keep in mind that Figure 7-1 does not represent silicon volume (i.e., it represents study project participants).
One interesting observation from this year’s study is the continue increase in design projects working on designs less than 1M gates. This is due to a number of projects working on smaller sensor chips for IoT and automotive devices. This can potentially yield some interesting results in the study.
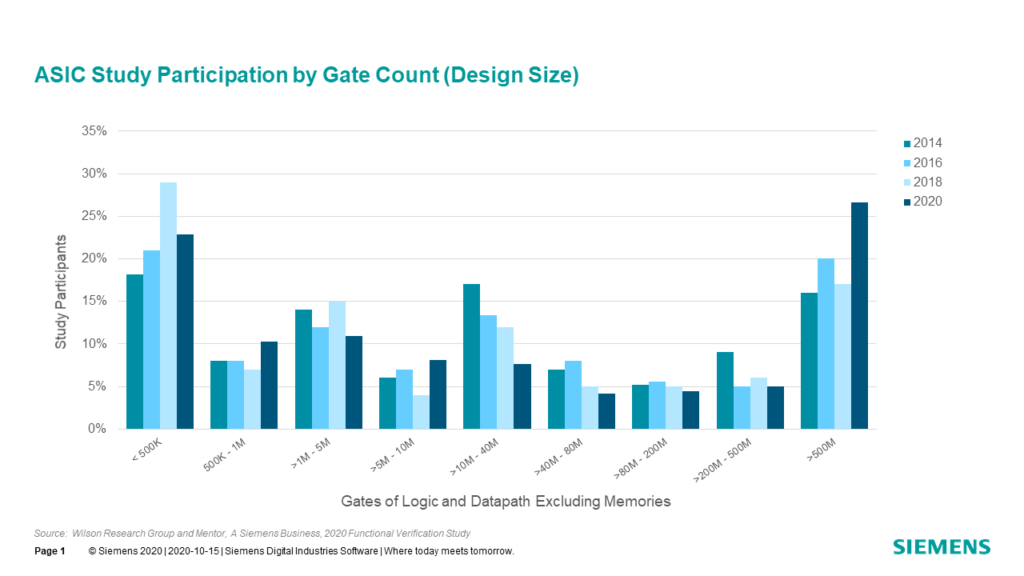
A key takeaway from Figure 7-1 is that the electronic industry continues to move to larger designs. In fact, 36 percent of today’s design projects are working on designs over 80M gates, while 31 percent of today’s design projects are working on designs between 1M gates and 80M gates.
But increased design size is only one dimension of the growing complexity challenge. One industry driver that has had a substantial impact on IC/ASIC design and verification complexity is the emergence of new layers of design requirements (beyond basic functionality), which did not exist years ago, for example, security requirements, safety requirements, and requirements associated with hardware-software interactions in embedded processor designs.
IC/ASIC Embedded Processors
What has changed significantly in design since the original Collett studies is the dramatic movement to SoC class of designs. In 2004, Collett found that 52 percent of design projects were working on designs that contain one or more embedded processors. Our 2020 study found that 68 percent of design projects were working on designs with embedded processors, as shown in Figure 7-2. In 2016 we found that 73 percent of projects were working on the designs with embedded processors? So why the decrease? Well, again, we saw a significant increase in projects working on smaller designs (e.g., less than 100K or less than 500K gates). In this case, this large increase of smaller designs has had an overall impact on the number of projects working on designs containing embedded processors. If we ignore these smaller designs and only look at designs greater than 1M gates we did not see a statistically significant change in the number embedded processors from 2016 to 2020.
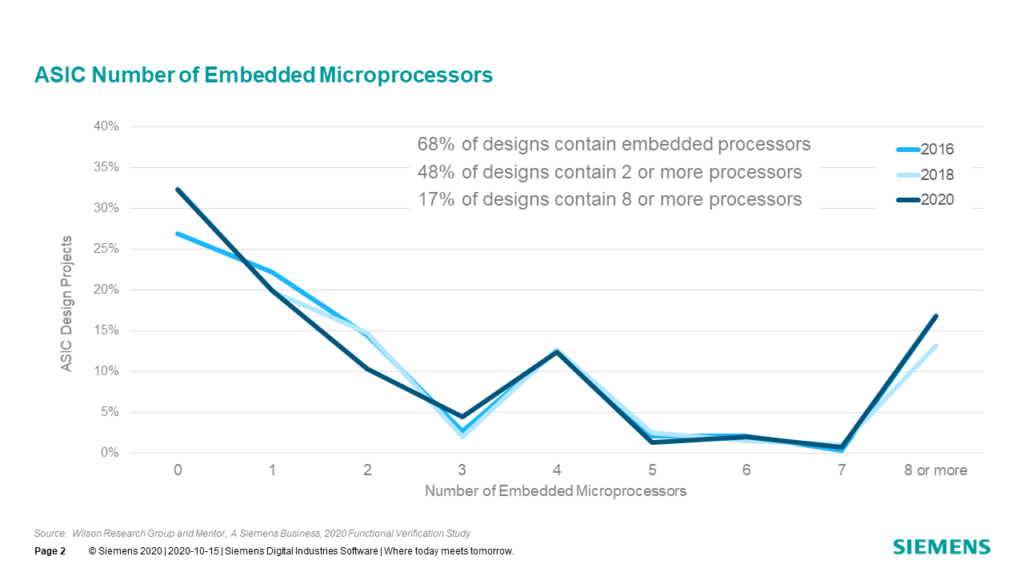
Another interesting trend is the increase in the number of multiple embedded processes in a single SoC. For example, 48 percent of design projects today are working on designs that contain two or more embedded processors, while 17 percent of today’s designs include eight or more embedded processors. SoC class designs add a new layer of verification complexity to the verification process that did not exist with traditional non-SoC class designs due to hardware and software interactions, new coherency architectures, and the emergence of complex network on-a-chip interconnect.
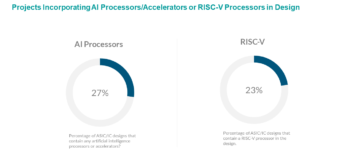
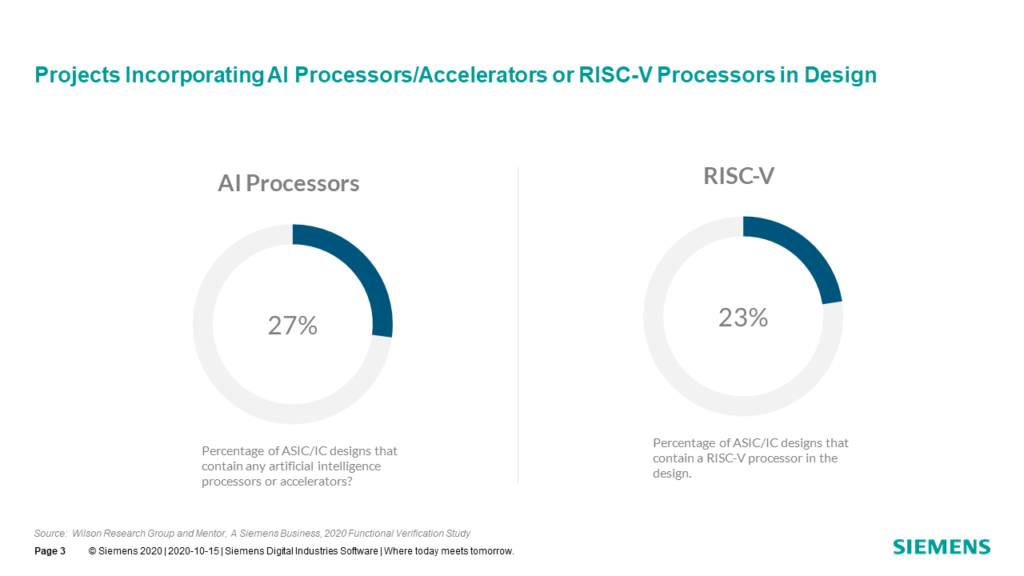
IC/ASIC Designs Incorporation AI and RISC-V Processors
Our 2020 study, for the first time, tracked the number of IC/ASIC projects that have incorporated a RISC-V processor in their design, which was 23 percent, as shown in Fig. 7-3. In addition, we tracked the number of IC/ASIC projects that have incorporated some type of AI accelerator processor (e.g., TPU, etc.), which was 27 percent.
IC/ASIC Security Features
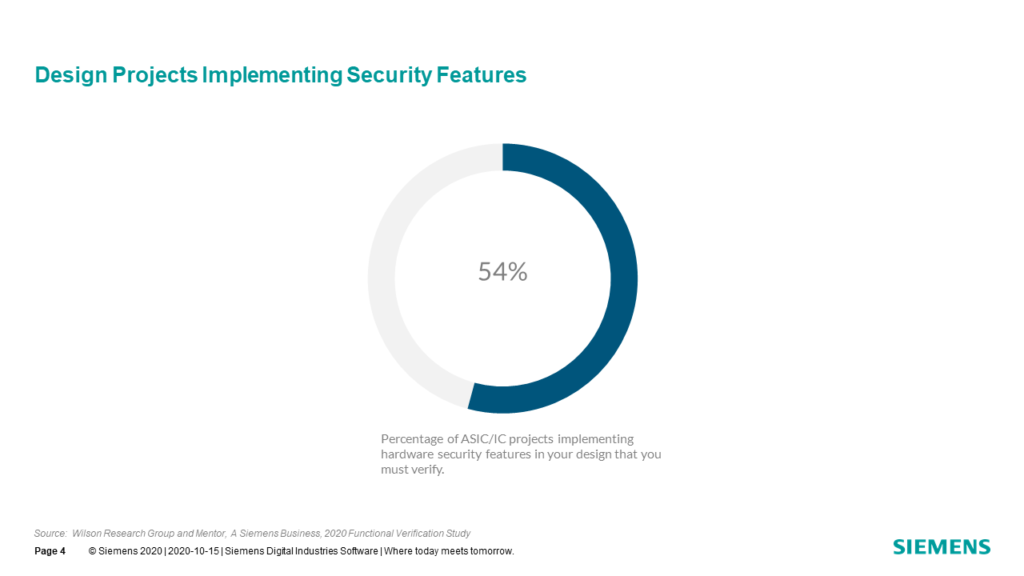
Many projects are implementing security features in their designs, as shown in Fig. 7-4. Examples of security features include security assurance hardware modules (e.g., a security controller) that are designed to safely hold sensitive data, such as encryption keys, digital right management (DRM) keys, passwords, and biometrics reference data. These security features add requirements and complexity to the verification process.
IC/ASIC Safety-Critical Design
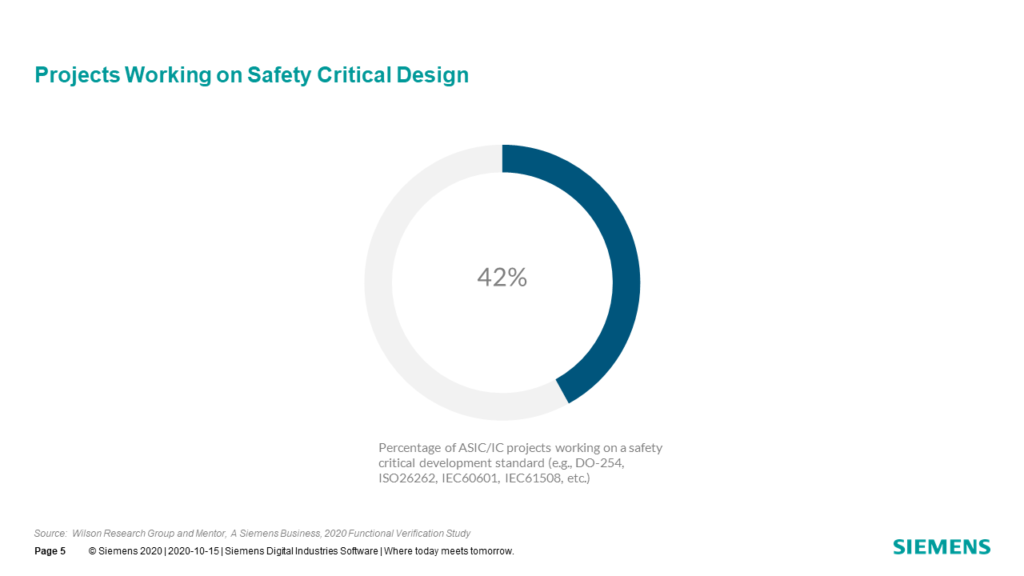
Another example of increasing requirements contributing to complexity relates to safety-critical designs. In Fig. 7-5, we see an increase in the number of IC/ASIC projects working under one of multiple safety-critical development process standards or guidelines.
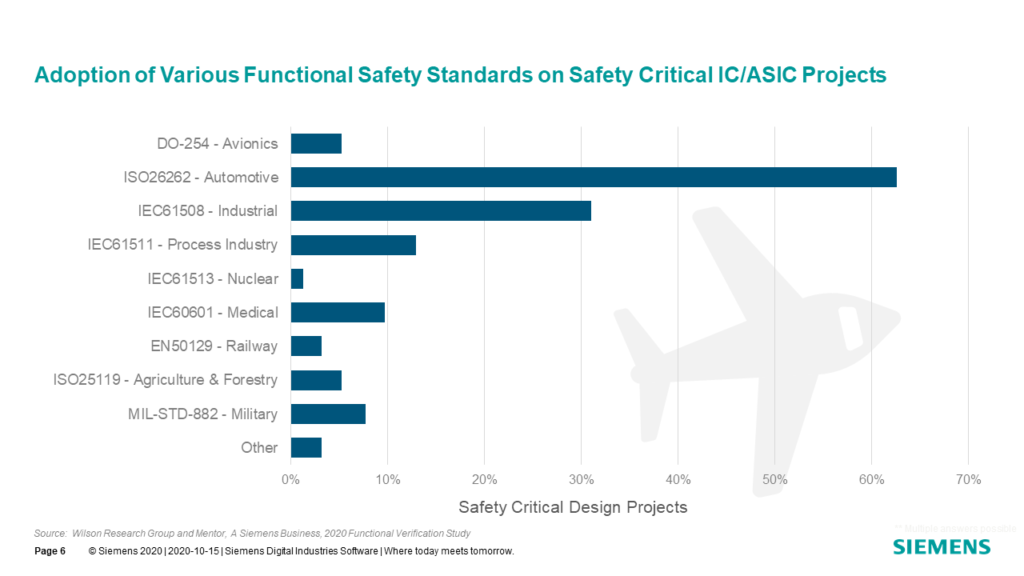
For those projects working under a safety-critical development process standard or guideline, in Fig. 7-6 we show the specific breakdown for the various standards within this group. Note that some projects are required to work under multiple safety standards or guidelines. For example, IEC61508 and IEC61511.
The key takeaway from this blog is that IC/ASIC designs are growing in complexity, which impacts verification effort and effectiveness.
In my next blog, I plan to discuss the growing IC/ASIC design project resource trends due to rising design complexity.
Quick links to the 2020 Wilson Research Group Study results
- Prologue: The 2020 Wilson Research Group Functional Verification Study
- Understanding and Minimizing Study Bias (2020 Study)
- Part 1 – FPGA Design Trends
- Part 2 – FPGA Verification Effectiveness Trends
- Part 3 – FPGA Verification Effort Trends
- Part 4 – FPGA Verification Effort Trends (Continued)
- Part 5 – FPGA Verification Technology Adoption Trends
- Part 6 – FPGA Verification Language and Library Adoption Trends
- Part 7 – IC/ASIC Design Trends
- Part 8 – IC/ASIC Resource Trends
- Part 9 – IC/ASIC Verification Technology Adoption Trends
- Part 10 – IC/ASIC Language and Library Adoption Trends
- Part 11 – IC/ASIC Power Management Trends
- Part 12 – IC/ASIC Verification Results Trends
- Conclusion: The 2020 Wilson Research Group Functional
- Epilogue: The 2020 Wilson Research Group Functional Verification Study



Comments