Optimizing DFT efficiency: Essential guidelines for SSN Bus Width and EDT channels
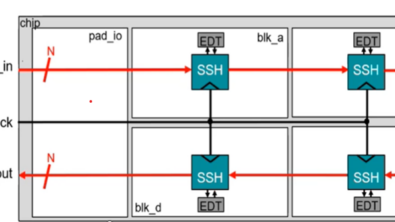
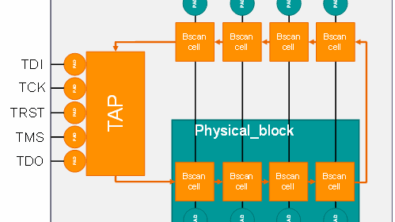
For an SSN design, only the SSN bus data in, SSN bus data out, SSN bus clock, and the TAP pins are needed for ATPG, since the SSN is programmed using IJTAG.
A wide high-speed SSN data bus requires physical resources since the default SSN bus clock frequency is 400 Mhz.
Correctly sizing EDT with SSN is very important since it can reduce the scan data volume per core up to 2.5X compared to a non-SSN design.
SSN bus width: The general recommendation for the is to reuse the same number of GPIO used for EDT channels (scan in/out) without SSN.
The SSN data_in and data_out ports should be symmetrical.
To determine the number of EDT channels: Tessent can help determine the number of EDT channels where test coverage loss is negligible.
For non-identical cores: Use symmetric EDT.
For identical cores:
Use asymmetric EDT: With more input channels, ability to data throttle between cores becomes easier.
Keep the number of output channels small
For more details please take look at Knowledge Base Article called Tessent SSN Bus width and EDT channel guidelines