Smarter, better, faster: How to benefit from AI and Reinforcement Learning to augment your Battery Energy Storage System (BESS)
As the global energy landscape shifts toward renewables, the need for intelligent energy management systems becomes increasingly critical. One of the most promising innovations in this space is the integration of “Battery Energy Storage Systems” (BESS) with AI-driven smart controllers, particularly those trained using “Reinforcement Learning” (RL). So that you can optimize your Battery Energy Storage Systems with AI-powered smart controllers and see directly the benefits using such approaches practically.

Let’s discover together the 3 steps needed to convert your digital twin from a BESS plant model into an augmented system with an optimal controller automatically generated, with no user interaction nor brainstorming and no coding. The best controller comes directly out-of-the-box, it’s a matter of a few hours combining two SIEMENS softwares: 1.- Simcenter Amesim for the digital twin of the physical system, and 2.- Simcenter Studio for the Reinforcement Learning. That’s it, that’s the way it is !
Challenges of AI-based solutions for smart BESS
There are a couple of challenges to be tackled when implementing the BESS onsite. Typically, we can find these usual challenges for balancing the supply, demand, and price:
- The wind energy, while clean and abundant, is inherently variable. Its generation depends heavily on weather conditions -especially the wind speed- which fluctuate unpredictably. This variability poses a challenge for grid operators and energy providers who must balance supply and demand while maintaining grid stability and minimizing costs.
- The wind energy is slightly more unstable than solar energy in the sense that for a specific location, the sun always appears at sunrise and goes down at sunset. Then it’s a matter of variations in weather conditions: sky can be cloudy, we can get a higher turbidity factor when particles are more present, … Still the windy conditions are usually much more variable over the day, the seasons and the whole year.

So it makes sense to consider this renewable source of energy to investigate how much benefit we can get from Reinforcement Learning applied to BESS. Indeed, the Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) offers a solution by storing excess energy during periods of low demand and releasing it when demand and prices peak. However, determining the optimal times to charge and discharge these batteries is a complex task influenced by:
- Real-time electricity prices
- Grid load conditions
- Weather forecasts
- Historical wind generation patterns
To tackle this complexity, researchers and engineers are turning to Reinforcement Learning, a branch of AI where agents learn optimal strategies through trial and error within simulated environments. In this case, the Reinforcement Learning agent is trained in two years of historical weather data, learning to predict wind energy availability and make informed decisions about when to store or release energy.
The Reinforcement Learning (RL)-powered smart controller continuously monitors:
- Wind speed forecasts to estimate upcoming energy generation
- Grid load levels to identify periods of high or low demand
- Electricity market prices to maximize economic returns
By learning from past patterns and adapting to real-time conditions, the controller can:
- Charge batteries when wind energy is abundant and prices are low
- Discharge batteries when grid demand spikes and prices are high
What is Reinforcement Learning (RL)?
Don’t be afraid, Reinforcement Learning (RL) is not as complex as it looks like. It’s just an interdisciplinary area of machine learning and optimal control concerned how intelligent agents should take actions in a dynamic environment to maximize a reward signal.
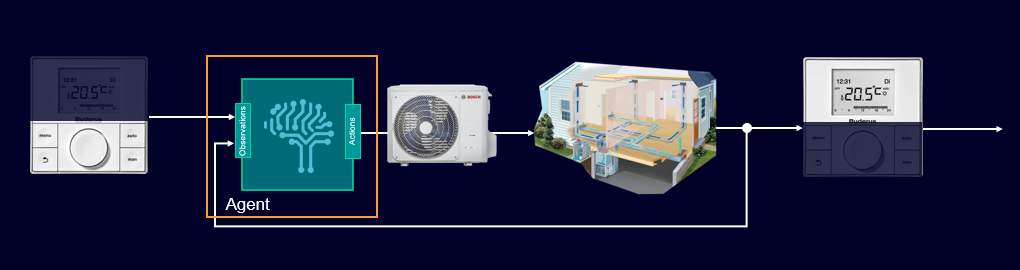
This approach translated into the context of System Simulation brings these 3 steps. Let’s consider first the simple illustration below, easy to understand. It is a domestic HVAC system with the following key characteristics:
- User goal: keep a comfortable temperature in the house
- Control inputs: ventilator speed, HVAC power request
- User inputs: temperature setpoint
- Information feedback: room temperature
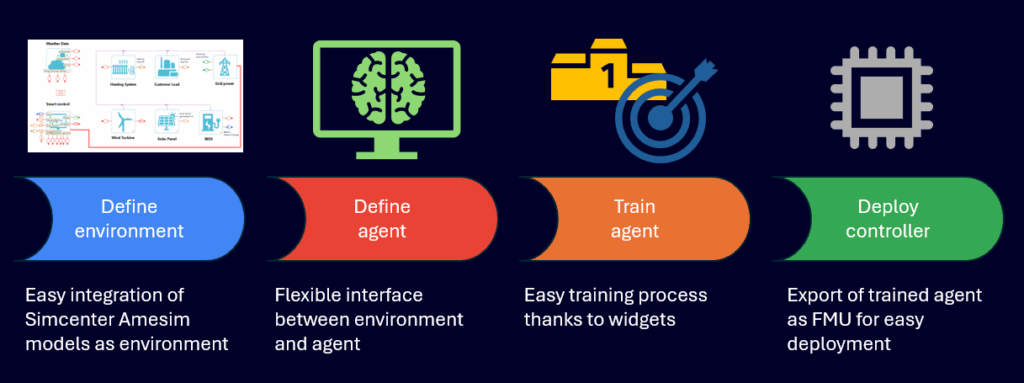
First, you need to provide the “environment”. It’s the system to be controlled (i.e. everything outside of the agent). It can be controlled through actions. And it can be observed through observations.

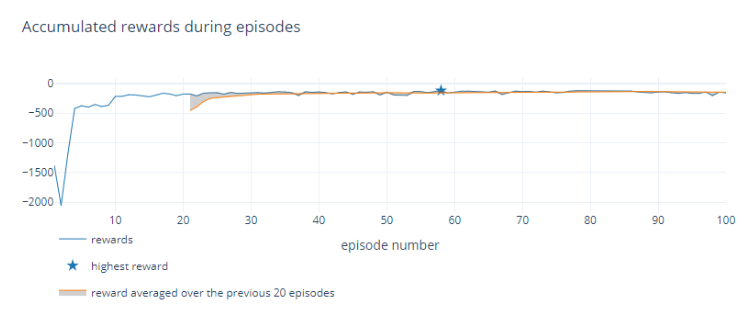
Then there’s the agent. It’s the part of the controller that will decide the actions to control the environment the best as possible. The training is done in episodes. Training an agent based on multiple scenarios is important for the convergence and generality of the agent.
The goal of the agent is to maximize the accumulated reward over all steps. The agent learns a policy by trial and error which actions the actor should apply for which observation of the environment, by observing the reward of the environment.
Once ready, the Reinforcement Learning can go for deployment. It’s the use of the policy trained by the agent as a controller by exporting it to a FMU (Functional Mockup Unit). It does not need to be executed within the same environment. E.g. the training can occur on a low fidelity model to be used in a higher fidelity system.

Let’s see how to implement this Reinforcement Learning approach practically for our BESS use case.
System simulation is a perfect enabler
The good thing with System Simulation is its ability to represent a complete system with a selection of key components. Thanks to its abstraction level, it’s easy to get a whole system and to execute it in a few seconds or a couple of minutes, no more. It’s a great advantage in the case of training where multiple scenarios have to be investigated. You don’t need weeks or months of computation, everything can be launched and delivered within the same day so that your optimal controller is ready quickly.
Let’s consider our BESS system with its input subsystems and output loads.
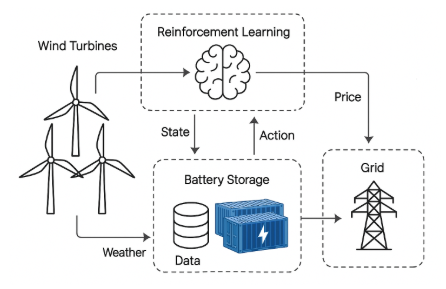
Basically, the diagram overview includes:
- Wind Turbines: Generate renewable energy based on weather conditions, especially wind speed.
- Weather Data Input: Historical and real-time weather data feed into the Reinforcement Learning agent.
- Reinforcement Learning Agent: Trained in 2 years of weather data, it predicts wind energy availability and optimizes battery control decisions.
- Smart Controller: Executes the Reinforcement Learning agent’s decisions to charge or discharge the battery.
- Battery Energy Storage System (BESS): Stores energy when prices are low and releases it when prices are high.
- Grid Interface: Connects the BESS to the power grid, responding to load and price signals.
This schematic representation is directly reflected in the Simcenter Amesim sketch where anyone can recognize the same layout. The main difference is the use of a signal bus (see the red bold line) to transport multiple signals within one single transmission line.
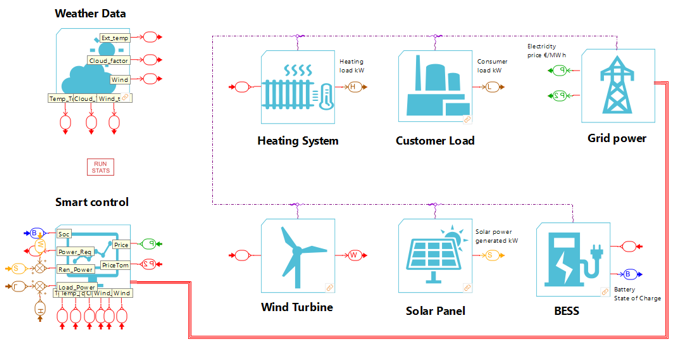
The digital twin is now ready. Let’s go the training and reward steps to get an optimal smart controller in a couple of clicks.
Few steps to go: training and reward
The agents from Reinforcement Learning can find out the optimal control strategy and parameter settings, just connecting Simcenter Amesim (for the digital twin of the physical system) with Simcenter Studio (for the reinforcement learning process). To get automatically the improved controller as an FMU (Functional Mockup Unit), ready for deployment back in the plant model.
The Reinforcement Learning agent is trained in a simulated environment that mirrors real-world conditions using mainly the historical weather data (wind speed, temperature, …).
The simulation allows the agent to learn optimal strategies without risking real-world assets, and once trained, the model is deployed to control the BESS in real-time.
We can compare our two controllers to estimate the benefits:
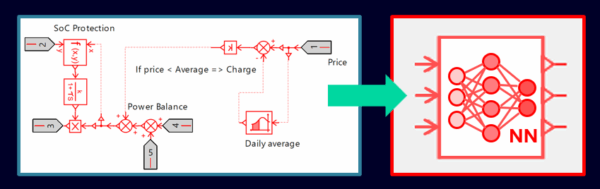
- The rule-based controller (left). It’s manually defined from knowledge. The control logics is fixed, with possible variations on a few parameters. It’s a simple strategy depending on the State of Charge (SoC) and price evolution. Basically, we define:
- If the current energy price is lower than the mean value of energy price during the week, the energy is stored into the BESS
- Otherwise, the energy is taken from the BESS and delivered to the grid, until BESS SoC reaches 5%
- The neural network controller from the Reinforcement Learning (right). It’s automatically obtained with no experience needed, except the right selection of the appropriate Reinforcement Learning algorithm. It automatically gets the best control strategy after its learning process with trial and error.
The agent is trained on short period with a random initial “SoC” (state of charge) in a given random week out of a two-year period thanks to the weather data provided for 2022 and 2023.
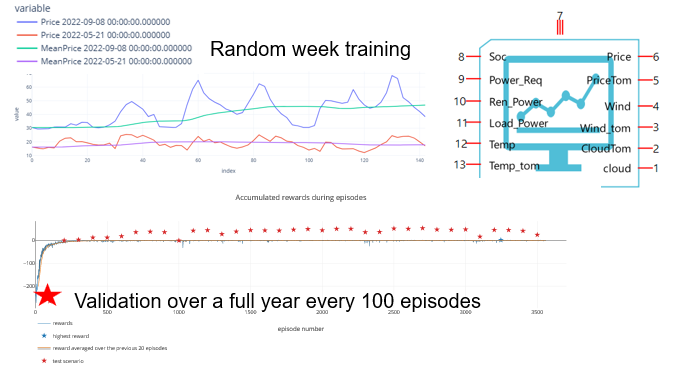
Then every 100 trainings, it is evaluated for a complete new year (2024) that it has never seen before:
- The inputs of the Neural Networks are the current power demand, the current power generation, the current weather conditions, the next day weather, the current SoC, the current price, and the next day price .
- The output is the battery power.
The agent takes a new decision every 10 minutes.
Real-world BESS use case with RL
Let’s check the typical results obtained for a real-world scenario. We compare the two controllers to measure the benefits using Reinforcement Learning.
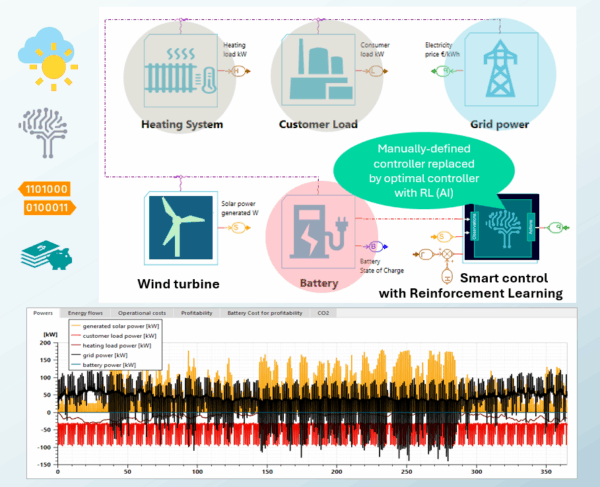
The configuration for exploration (training/validation) of the smart controller (AI/RL) is the complete BESS system with the wind turbine for renewables . It’s used to verify that the controller works well and is fully efficient and predictive.
- The objective is to find out the optimal control strategy for 1 configuration with weather forecast (future) and energy price evolution.
- The reward is the reduction of the energy bill (so the increase of the associated benefits due to savings) and the reduction of the carbon emissions.
- The exploitation can be done by exporting the optimal controller as an FMU onto the hardware device, connected to the weather forecast.
Below is what happens practically for the training and reward process in Simcenter Studio:
The goal is to get an optimal controller quickly. Let’s check on a real-world scenario testing the last year 2024 of weather conditions to formally evaluate how it behaves. Just to confirm it’s efficient and well predictive.
Key benefits for users
We simulate one complete year (2024) which is basically 365 days. We compare 3 configurations as described below:
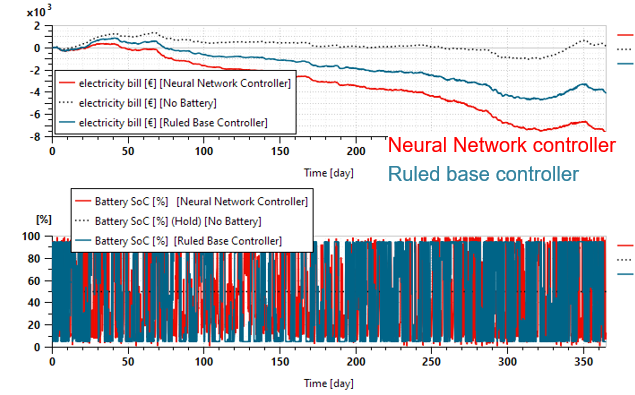
- Configuration #0 : [No battery] (dotted grey curve – reference) is the results without any BESS considered.
- Configuration #1 : [Ruled-base controller] (blue curve) is the previous case we had with a BESS introduced and its control defined manually,
- Configuration #2 : [Neural Network controller] (red curve) is the latest case we tested with a BESS introduced and its control found out automatically with Reinforcement Learning (AI/RL).
There’s no doubt. The comparison proves that the Reinforcement Learning controller is much better than the legacy one, which was defined manually based on quite simple rules known by experience.
We clearly see the benefits using the Reinforcement Learning controller since the electricity bill is strongly reduced after 1 year compared to the other approaches. It’s important to note that the lifespan for such BESS systems is typically 20 years, so any gain obtained over 1 year will be amplified significantly over such a long period of time. Well done, we see great benefits using Reinforcement Learning!
Going further
We can consider the benefits of AI-Optimized BESS for various KPIs (key performance indicators) like its economic efficiency, the grid stability, the sustainability or its scalability when deployed across multiple sites and adapted to other renewable sources like solar.
While looking ahead, as AI continues to evolve, we can already notice that the integration of RL-based controllers with BESS will become more sophisticated, potentially incorporating real-time weather sensors, predictive analytics, and even collaborative multi-agent systems across distributed grids.
This convergence of renewable energy, battery storage, and artificial intelligence marks a transformative step toward a smarter, greener, and more resilient energy future.
It opens the door to “Simulations in Operations” with digital twins and AI-based controllers to take the right informed decisions live in operations. It’s “Simulation for Service” thanks to physics-based-AI.
As usual, System Simulation definitely helps you and your company be successful in your BESS journey thanks to digitalization, with system integration and smart controls.
Learn more about Siemens Simcenter Amesim
Simcenter Amesim is the leading integrated, scalable system simulation platform, allowing system simulation engineers to virtually assess and optimize the performance of mechatronic systems.


