Embrace the digital twin in manufacturing: Deliver performance, reliability and efficiency
Embracing the digital twin approach in manufacturing is no longer some far-flung promise. Gartner, in 2017, predicted that by 2021, half of the large industrial companies will use digital twins, resulting in those organizations gaining a 10% improvement in effectiveness. While it is true that large companies are embarking on the digital twin journey with the pilot project, the scale of digitalization’s impact encompasses the organization, its employees, society, the global economy and even the sustainable future of the planet. The organization can respond to market changes more rapidly. Product functional attributes (performance, reliability, energy efficiency) can reach new heights while eliminating performance uncertainties and manufacturing waste. Spooked or excited?
Join our free live webinar – “Concept to realization: Digital Twin in Manufacturing” from a factory automation expert to learn more.
The digital future of the industry is very promising for manufacturers, consumers and society as a whole. Today’s products are becoming smarter, more personalized. They’re becoming intricate systems of systems, challenging product manufacturers to harness layers of complexity and data. The fourth industrial revolution (4IR) is upon us and is enabling the digital twin in manufacturing.
The four industrial revolutions
Our civilization has come a long way from being an agrarian dependent economy to a machine dominant society. In this evolution, there were certain key industrialization milestones and the progress can be classified by four industrial revolutions. At each of the four industrial revolutions, there was a clear shift in productivity, efficiency, livelihood improvements and global economic progress.
The first industrial revolution started with the extraction of coal and the utilization of steam and water power to operate textile mills setting the stage to mechanize all moving parts. The arrival of the new forms of energy: electricity, oil and gas prompted the second industrial revolution enabling factories, machines, and the concept of mass production. Around 1960, the invasion of electronics paved the way for industrial automation and process optimization, an outcome of the third industrial revolution.
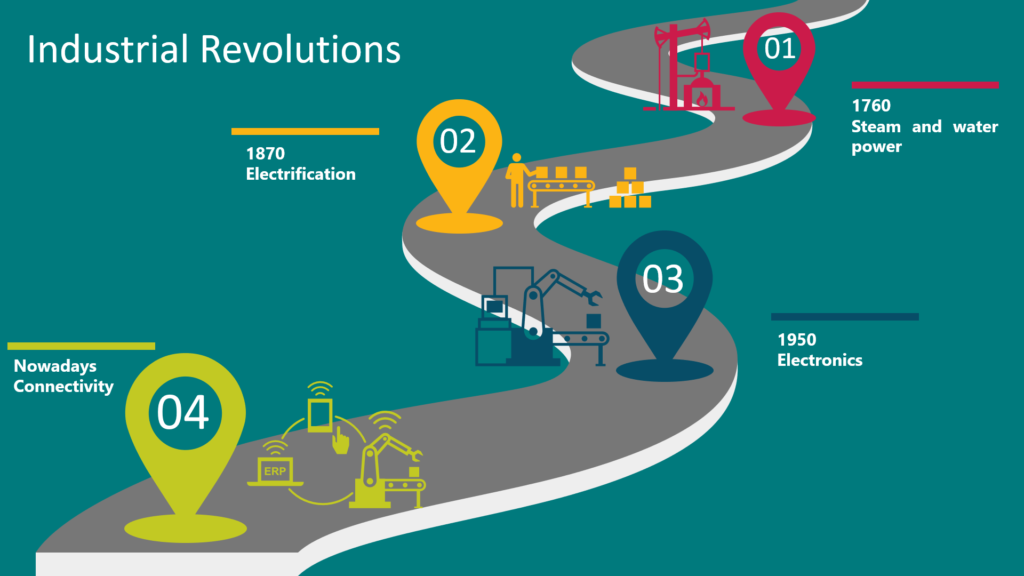
Nowadays the fourth industrial revolution (4IR) or Industry 4.0 is upon us and will impact all industries and every sector. The arrival of 5G, designed for ubiquitous connectivity, combined with the convergence of technologies – automation, IoT, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and accurate multiphysics digital-mockups provide enormous opportunities to advance society.
Birth of the digital twin
Perhaps the first use of the phrase “digital twin” is seen in the reports published by NASA and the US Air Force in the year 2012. In the report, the term “digital twin“ is defined as follows – a digital twin is an integrated multiphysics, multiscale simulation of a vehicle or system that uses the best available physical models, sensor updates, fleet history, etc., to mirror the life of its corresponding flying twin.
Though the report addresses the aerospace industry, the underlying approach can be applied to all industries. Decreasing sensor costs, abundant connectivity, and cloud-based computation democratizes the digital twin for all manufacturers so that even small and medium enterprises can fully exploit the Industry 4.0 digitalization potential.
Maturing simulation and testing solutions to enable cyber-physical systems
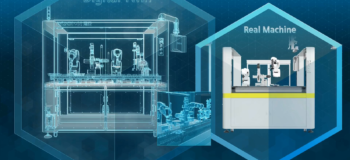
While there exist substantial resources for the successful implementation of the digital twin in manufacturing, a step-by-step approach to digitalize machines on the shop floor is still lacking. Siemens’ factory automation experts took a tactical approach by creating a digital twin of a packaging machine developed at Technology Application Center (TAC) in Piacenza, Italy and will be holding an online session to demonstrate the true potential that simulation and testing technologies play in realizing digital twins in manufacturing. Below, a sneak-peak of the packaging machine.
Are you working for a machine manufacturer in the discrete or process industries? Is your organization serious about digitalization and exploiting the potential that Industry 4.0 offers? Then I warmly welcome you to register for the upcoming webinar on the topic “Concept to realization: Digital Twin in Manufacturing”. From system engineering aimed at component sizing to EMC/EMI issues in Industry 4.0 to augmented reality for remote machine maintenance, we will be covering all aspects of the digital disruption that is happening today.
Sources:
- The Fourth Industrial Revolution, Klaus Schwab


