Unlocking post-tapeout flow scalability and performance with cloud computing

By Bassem Riad
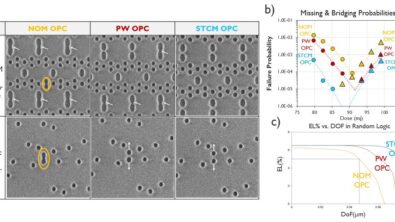
As process geometries continue to shrink, computational lithography demands increasingly powerful and abundant CPU resources to support more complex algorithms and higher-precision device models. Running post-tapeout flow (PTOF) jobs such as Optical Proximity Correction (OPC), Mask Process Correction (MPC), and Mask Data Preparation (MDP) pushes computational limits of traditional on-premises resources, resulting in unpredictable workloads and significant scaling challenges.
The Siemens EDA Reference Environment for AWS answers these challenges with key optimizations, including dynamic scaling to maximize resource utilization and runtime efficiency, along with hardware monitoring for fine-tuning instance types. Cloud Flight Plans guide users make the transition to cloud, and alongside this platform, Siemens EDA provides powerful tools for cluster management and massive scalability.
At the recent SPIE 2024 Advanced Lithography + Patterning conference, we had the chance to present our work on harnessing cloud computing for PTOF jobs in semiconductor manufacturing. During our presentation, we demonstrated how leveraging cloud computing can provide a seamless and cost-effective solution. For a deep dive into this PTOF cloud flow, please see the technical paper, Crush Semi-manufacturing runtimes with Calibre in the cloud.
Cloud: The solution to a long-standing problem
Cloud computing is a proven answer to the compute challenges EDA companies have been facing for years. Here are a few reasons cloud computing is advantageous (and becoming imperative) in the post-tapeout flow:
- Cost efficiency: Eliminating upfront investments in favor as pay-as-you-go pricing models and the ability to tap into AWS spot instances for even greater savings.
- Scalability: Dynamically scale resources up or down in minutes to match fluctuating workloads, eliminating bottlenecks.
- Unmatched speed and agility: Adjust cluster sizes in minutes, compared to the weeks or months required to expand physical infrastructure.
- Global reach: Gain access to cloud resources worldwide, enabling seamless and secure collaboration across teams, partners and regions.
- Customized computing: Choose from over 400 types of compute instances tailored to your PTOF job needs, including CPU, core count and memory configurations.
Siemens EDA and AWS Cloud Flight Plans
In July 2023, AWS and Siemens EDA established a strategic collaboration agreement to accelerate the migration of EDA workloads to AWS. This partnership introduced Cloud Flight Plans, which offered best practices, infrastructure-as-code scripts, and other best-known methods (including the paper referenced in this post) to simplify deploying and running EDA workloads. Users can scale seamlessly to hundreds of thousands of cores, reducing capital investment while enabling faster production. AWS also facilitates secure global collaboration across the semiconductor ecosystem, including fabless companies, IP providers, foundries and other partners.
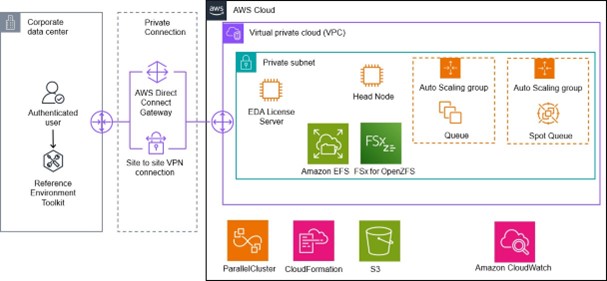
The Reference Environment
The Siemens EDA Cloud Reference Environment for AWS is a toolkit that manages jobs inside a secure chamber on AWS. It uses AWS ParallelCluster to deploy the AWS services, with the Slurm job scheduler handling job orchestration. Slurm dynamically scales compute nodes based on workload, adding resources when needed and scaling back to use minimal resources when idle. Pre-configured templates make it easy for IT and CAD teams to quickly launch an optimized cloud environment, including support for Calibre MTflex distributed computing. It’s a ready-made setup for efficient, scalable cloud operations.
CalCM+ in the cloud
The Calibre Cluster Manager (CalCM) was originally designed to monitor CPU demand and optimize cluster utilization for on-premises applications and has been successfully used for over a decade. With new capabilities, CalCM has evolved into the AI-powered CalCM+ for cloud environments, and is ideal for execution in the Siemens/AWS Reference Environment. Offering enhanced flexibility and an updated dashboard to monitor cloud resources and costs, CalCM+ includes key features including:
- Adaptive resource management: Dynamically allocates cluster nodes and licenses based on job requirements, priorities and hardware availability.
- Comprehensive activity tracking: Records job performance, hardware usage and network conditions for future analysis.
- Interactive monitoring: Provides a dashboard to track resource utilization and job progress in real-time.
In cloud settings, CalCM+ works alongside the AWS Reference Environment, adjusting job scheduling and releasing idle resources to reduce costs. Recently, we’ve added new cloud capabilities:
- AUTOREVOKECYCLE: Improves CPU utilization by reclaiming unused resources.
- Cloud cost app: Estimates real-time job costs based on AWS pricing (recently prototyped, available only to cloud users).
- Data analysis tools: Predicts runtime and memory needs for optimal instance selection.
- Spot notifier tool: Enables seamless use of AWS spot instances, even during interruptions (see below for more on spot instances).
Bonus cost savings with spot instances
Amazon EC2 spot instances let you use spare AWS cloud capacity at a fraction of the cost—up to 90% less than on-demand prices.
But here’s the catch: Spot Instances can be taken back by AWS anytime regular demand spikes. This isn’t an error; it’s just how Spot Instances work. That’s why they’re best suited for tasks that can handle interruptions. AWS gives a two-minute warning before shutting down a Spot Instance, so you can wrap up tasks and remove the terminating Spot Instance from the job.
For Calibre users, the “Calibre Spot Notifier” tool (currently in beta) helps manage these interruptions. It monitors AWS’s termination signals and gives CalCM enough time to shift workloads to other remote hosts without causing errors. Just make sure critical services aren’t running on Spot Instances—stick to pure computation tasks that can easily be re-launched.
With the right setup, you can take full advantage of Spot Instances without disruptions, and see significant cost savings in the process.
Calibre FullScale
Calibre FullScale is ideally suited for the Siemens/AWS Reverence Environment. It is a high-performance platform built for post-tapeout workflows like OPC, RET, and MDP, leveraging thousands of CPUs for maximum efficiency. It splits jobs into independent tasks that run in parallel and groups dependent tasks to process together seamlessly. By retaining some layout hierarchies and accessing data directly (instead of using a database), Calibre FullScale speeds up operations but requires high network speed (at least 10GB/sec). Best suited for flattened layouts common in post-tapeout flows, Calibre FullScale excels by breaking large jobs into small, optimized tasks using smart algorithms. For heavy workloads, the PFSDB option can reduce network congestion by leveraging a fast temporary storage, resulting in smoother and faster processing.
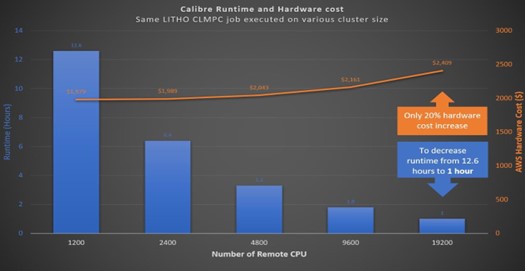
The cost vs. runtime equation
One of the key advantages of cloud computing, especially on the tight deadlines commonly post-tapeout, is the ability to strike a balance between runtime and cost. Siemens EDA’s benchmarks show that doubling the CPU count can dramatically reduce runtime with only a slight increase in cost. This flexibility allows manufacturers to prioritize speed for urgent projects or save money on less time-sensitive tasks.
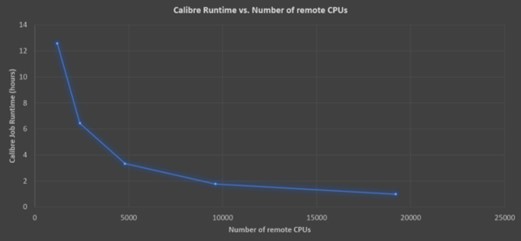
With the virtually limitless CPU resources available in the cloud and the exceptional scalability of lithography simulations, achieving any desired runtime is virtually within reach.
Looking ahead: A new era for semiconductor manufacturing
The partnership between Siemens EDA and AWS is more than just a technological collaboration—it’s a blueprint for the future. But it’s only a starting point. Tools like CalCM+ and Calibre FullScale further optimize performance, scalability and cost, making cloud computing the optimal answer at crunch time.
If you’re a process engineer, lithography technician, foundry manager, or if you’re on the design side and intrigued by the power of cloud computing and its role in computational lithography, this shift is worth exploring. Dive into the full technical paper, Crush Semi-manufacturing runtimes with Calibre in the cloud to discover how Siemens EDA and AWS offer manufacturers the tools they need for maximum productivity when it’s needed most.
If you are a Siemens customer, you can access our most recent SPIE presentation Cloud Flight Plan for Post-Tapeout Flow Jobs on Support Center.