Reshaping the world with digital manufacturing [VIDEO]

Updated August 28, 2024
An open dialogue with Zvi Feuer about the future of manufacturing.
Watch the interview [VIDEO]
Let’s face it, without manufacturing, our lives would be very different.
Manufacturing impacts all of us and improves our lives. Every single day, we interact with countless objects, from our earphones containing the tiniest microchips to the largest aircraft soaring in the sky. What is common among them? They are all the result of manufacturing.

This sector, employing over 200 million people globally and generating a staggering $8.6 trillion in revenue, is the backbone of our economies. But its significance does not stop there. Manufacturing is also the engine of innovation, pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
Digital manufacturing: The cornerstone of modern manufacturing
Today’s manufacturing differs greatly from a few years ago.
Digital technologies are reshaping the manufacturing industry, becoming an integral part of modern production. An increasing number of companies are using sophisticated simulations and visualizations of products and processes before they are brought to life or before a single machine is turned on. Leveraging comprehensive manufacturing data, manufacturers can anticipate and refine production workflows, ensuring unparalleled precision and efficiency. This digital transformation not only optimizes production but also significantly improves sustainability, setting the stage for the future of manufacturing.
This fundamental transformation is enabled by digital manufacturing. To better understand what is driving these changes, we recently sat down with Zvi Feuer, Senior Vice President of Digital Manufacturing Software, and CEO of Siemens Digital Industries Software in Israel.
“Digital manufacturing integrates technologies like IoT (Internet of Things), AI (Artificial Intelligence), cloud computing, and big data analytics into production processes, driving efficiency, cost reduction, and faster cycles through real-time monitoring and automated decision-making. It improves the manufacturing capabilities of companies of all sizes in all industries,” said Zvi. He then continued to explain that digital manufacturing enables products to be designed, simulated and produced seamlessly in the digital world before doing so in the real world. This is not merely a trend, but a fundamental transformation that is being embraced by all industries, like automotive, aerospace, electronics and medical sectors.
Many businesses are realizing substantial long-term benefits, such as achieving time-to-market and reducing costs by minimizing expensive downstream changes. This is made possible by creating simultaneous definitions of both product designs and manufacturing processes. This approach allows industries to digitally define entire manufacturing workflows, fostering seamless collaboration between all the stakeholders, including designers, engineers, and manufacturing staff.
The ever-changing digital manufacturing landscape
The manufacturing landscape has constantly evolved. Zvi Feuer reflects on the transformations he has witnessed in manufacturing since his beginnings on the shop floor. He recalls how CNC machines were not only expensive but also challenging to operate. “I was not allowed to touch the machines for the first six months after I started working in manufacturing. “Today,” he reflects, “machines and operations have evolved to be smarter and more accessible across the manufacturing sector. I see engineers that get notifications about the manufacturing process on their smartwatches.”
While digital transformation has significantly advanced product design, the same level of innovation has yet to fully permeate manufacturing processes. Embracing digital manufacturing holds the potential to streamline operations, optimize production efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance overall product quality through integrated simulations that help accelerate time-to-market for new products and innovations, real-time analytics, and collaborative tools. This shift not only promises greater agility and resilience in manufacturing but also paves the way for competitive pricing and sustainable practices, ensuring a robust future for global industry.

“You hardly can innovate just by doing design and then shipping things to another place. You need close proximity between product development and manufacturing, and the connection between the two is critical.”
-Zvi Feuer
Many companies worldwide have adopted computer-aided design (CAD) tools for digital product design and development, yet fewer have fully embraced digital transformation in manufacturing planning, production optimization, logistics, supply chain management, and service.
The focus now lies on digitalizing manufacturing and planning production facilities to enhance efficiency, effectiveness, resilience, and agility. This approach aims to increase production facility utilization and enable competitive manufacturing. Achieving this requires increased automation, the use of robotics, and smart operations with AI-empowered operators.
Emerging technologies are accelerating innovation in digital manufacturing
83% of manufacturers believe that smart factory solutions will revolutionize the way products are made within the next five years. The potential benefits of smart factories are vast, including significant gains in asset efficiency, labor productivity, and product quality, as well as substantial cost reductions and advancements in safety and sustainability.
-Deloitte Research Center for Energy & Industrials
An area where I see a big emphasis is digitalization of manufacturing and planning of the production facility to ensure that we are much more efficient, effective, resilient and agile to enable a much higher utilization of production facilities.
-Zvi Feuer, Senior Vice President, Digital Manufacturing, Siemens Digital Industries Software
Artificial intelligence (AI)
AI in digital manufacturing leverages artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance production processes, meeting the rigorous standards of demanding industrial environments. By handling vast amounts of machine data and detecting complex patterns, it accelerates digital and sustainability transformations at scale. Artificial intelligence improves decision-making and operational efficiency using advanced analytics and machine learning techniques, significantly enhancing the functionality of digital manufacturing solutions by streamlining production planning and execution and ensuring real-time quality control.

The use of AI in industrial applications is vast and transformative. Zvi described that Siemens is working on an AI-powered recipe builder that utilizes a large language model to automatically extract material, equipment, and procedural details from reference documents for the development of production processes for new medicines. By engaging with the digital copilot, users can refine the recipe, production steps, and equipment requirements, enabling the creation of a comprehensive bill of process (BOP) in the PLM system with a single click. This significantly streamlines the labor-intensive process of BOP creation. AI-driven quality control systems detect defects in real-time, ensuring higher product quality and reducing waste, driving the industry toward a smarter and more sustainable future. And this technology enables predictive maintenance by anticipating equipment failures, minimizing downtime, and ensuring higher product quality using real-time defect detection.
Industrial metaverse
The industrial metaverse creates immersive digital environments that mirror physical operations, enabling real-time collaboration and simulation. It is a concept of a digital world to mirror and simulate real machines and factories, buildings and cities, grids and transportation systems. By seamlessly integrating technologies like cloud and edge computing, industrial AI and digital twins, the industrial metaverse can optimize processes and drive sustainable practices, ultimately shaping the future beyond simulation.
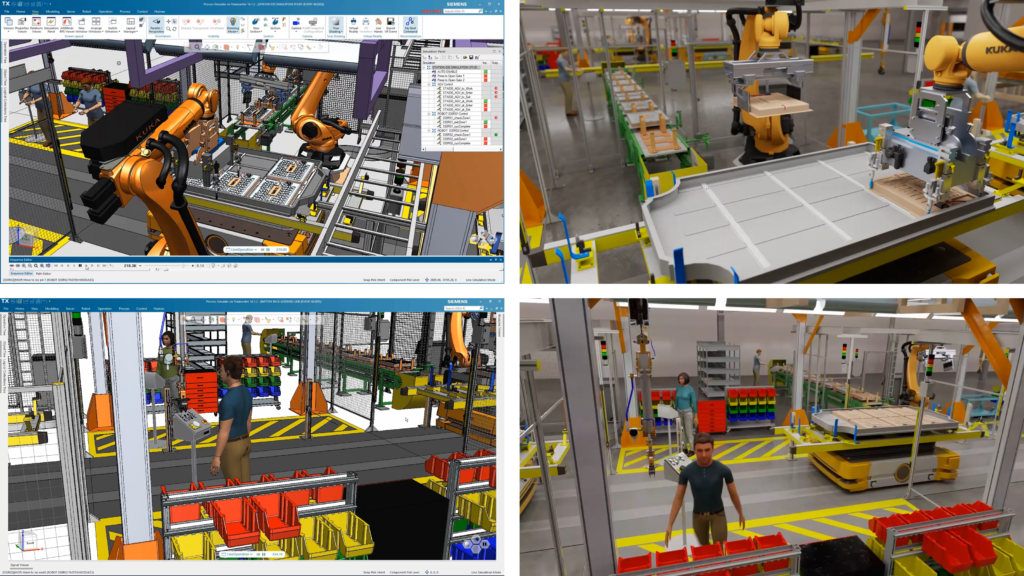
For example, the industrial metaverse has been instrumental in scaling battery production recently. With the help of a comprehensive digital twin built with software in the Siemens Xcelerator portfolio, interactions between robots, AGVs, and humans in the cell are simulated. This detailed model and simulation of the battery pack assembly line, where battery modules are integrated into the housing, are rendered in NVIDIA Omniverse software, which connects with Siemens digital manufacturing. The Omniverse platform provides realistic visualization with material mapping textures and integrates additional data such as building models and facility details, resulting in a high-end, interactive industrial metaverse experience.
Cloud computing
The shift to cloud computing is transforming manufacturing, especially for smaller companies, by simplifying the digitalization of manufacturing sites without the need for complex hardware installation, extensive IT teams, or large computer rooms. Cloud computing offers high capacity computing power, accelerating operations and enabling seamless integration of AI across diverse applications and processes. With cloud, manufacturing companies can efficiently scale their operations, optimizing resource utilization, enhancing overall productivity, and effectively managing costs while maintaining agility. This empowers them to strategically allocate resources to drive innovation and gain competitive advantage.
Cloud is an enabler to provide our customers with better service and to reduce their cost. This means that they can free up budget to buy software for other areas which today they do not cover. This enables them to do digitalization in a big way, but with a smaller amount of money, and to better collaborate with their customers.
-Zvi Feuer, Senior Vice President, Digital Manufacturing, Siemens Digital Industries Software
Introducing cloud-based modular solutions in manufacturing enhances flexibility and efficiency, perfectly aligned with the dynamic requirements of modern manufacturing environments. These solutions streamline operations and support anytime, anywhere access to efficient documentation and advanced collaboration tools. This capability not only optimizes productivity and responsiveness within manufacturing processes but also facilitates digital collaboration with internal teams and external stakeholders, including customers and partners. The result is enhanced agility, improved decision-making, and strengthened competitive advantage in a rapidly evolving market landscape, ensuring sustained growth and innovation.
Siemens has been using cloud technologies to develop software solutions that encompass applications such as process simulation and collaboration that enhance the productivity of simulation professionals. This enables faster collaboration with stakeholders, reduces documentation time by 20%, and facilitates efficient sharing of simulation outputs.

In another use case, Siemens and Salesforce have integrated their PLM and CRM solutions for service lifecycle management (SLM). This integration enhances the flow of service-related information throughout the product lifecycle, ensuring optimized service processes and improved customer satisfaction using accurate, real-time data sharing across design, engineering, manufacturing, and customer service stages.
Sustainability in manufacturing
The goal of sustainability in manufacturing involves achieving zero waste, zero downtime, and zero harm while minimizing environmental impact through low-cost, clean, renewable energy.
With this in mind, we asked Zvi about how manufacturing impacts sustainability. He emphasized, “Manufacturing demands a lot of energy and creates a lot of CO2 emissions. That’s going to be a challenge in the coming years: how to deal with these CO2 emissions and how to ensure that we are truly taking care of the environment, minimizing energy costs and consumption.”

Sustainability requires everyone in an organization to integrate sustainable practices. Understanding material impacts, energy usage, and environmental considerations is crucial. This holistic approach fosters faster, more agile, and creative problem-solving. Digital manufacturing facilitates streamlined production processes, minimizes waste, enhances quality control, and optimizes supply chain management while reducing environmental impact. By utilizing technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), data analytics, and automation, companies can achieve higher efficiency and reduce energy consumption in their manufacturing operations.
Integrating digital manufacturing technologies using a digital thread
A digital thread is a connected and traceable series of digitized and automated activities throughout the product or production lifecycle. It integrates data flow and connectivity across various stages, from design and manufacturing to maintenance and beyond. This framework ensures that data is accessible and actionable at every stage, creating a seamless and continuous flow of information that enhances productivity, innovation, and competitiveness during the manufacturing process.
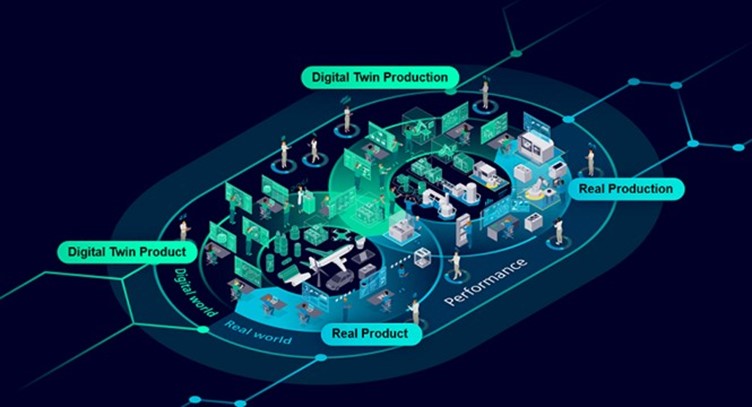
Digital threads in manufacturing streamline processes across the product lifecycle, ensuring seamless coordination from design to production. These threads consist of interconnected solutions from our software suite, designed to facilitate efficient communication and integration throughout every phase, including design, engineering, production, testing, and more. Customers recognize the value of this end-to-end connectivity but can adopt components incrementally, starting with individual products or partial solutions and expanding as needed. This scalable approach ensures smooth information flow between product development and the shop floor, showcasing the flexibility and effectiveness of digital threads. By integrating these capabilities, digital threads not only enhance efficiency but also enable real-time data exchange and decision-making, providing deep insights into performance metrics across the manufacturing ecosystem. Ultimately, they empower manufacturers to boost productivity, improve quality, foster innovation, and quickly adapt to evolving market demands and technological advancements.
For example, digital threads have played a crucial role in accelerating digital automation for an industrial additive manufacturing company serving the aerospace industry. Integrating several Siemens software’s enabled the company to replace outdated processes and scale rapidly from 10 to 60 projects and 200 work orders. This digital thread approach significantly improved traceability, visibility, and operational efficiency, preparing them to manage a potential 500% increase in business.
Curious to learn more about digital manufacturing? Learn about the secrets to success in digital manufacturing by reading the executive’s guide to digital manufacturing eBook now.


