Smart is Sustainable.

Topic 1 in our Blog Series, “Sustainability in Semiconductors. Every Detail Matters.”
Hannover Messe 2024, the world’s leading industrial trade fair happened April 22-26 in Hannover, Germany. Siemens is giving you a digital preview of the comprehensive range of solutions for semiconductor design and production on display at the event. Siemens’ theme this year: “Sustainable Digital Enterprise – Semiconductors” highlights how technology and industry ecosystem work together to achieve sustainable chip production.
Semiconductor processes are complex, and every detail matters from design to production in achieving sustainability. A world in critical need of a sustainable future needs smart manufacturing for semiconductors. The demand for smart technologies – phones, computers, medical devices, and transportation – continues to grow, so too does the responsibility to ensure their design and production is environmentally responsible.
The rapid expansion of the semiconductor industry, with chip production projected to nearly double by 2030, presents a looming environmental challenge.* Semiconductor plants, which typically operate continuously 24/7, contribute significantly to this challenge through high energy usage, chemical use, water consumption, and emissions of greenhouse gases and hazardous pollutants.
…but what if semiconductor companies could advance sustainable chip design and production processes to scale up with smart, secure operations throughout the product lifecycle – while minimizing their carbon footprint?
Sustainability is a journey, but the most important step is the first one. Designing for sustainability begins with the commitment to reduce the carbon footprint. Lowering energy consumption, eliminating waste generation, and reducing chemical usage are good places to start. Then comes next steps such as selecting environmentally friendly materials, less regulated substances, and sourcing alternatives to PFAS (per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances) to decrease the environmental impact. Next, we must take steps to safeguard the most essential resource of all, by incorporating water-efficient technologies to minimize high-volume usage and wastewater creation. Then comes steps like incorporating Digital Twins to plan and optimize fabs, and leveraging the Siemens FMCS (Facility Monitoring and Control System) to optimize resource and plant efficiency. And there are many other vital steps ahead.
What makes the journey even more challenging is pursuing sustainability while meeting unprecedented semiconductor demand. That’s where legacy methods fall short and where smart manufacturing begins.
Why? Traditional methods fall short in addressing these complex challenges. We need a new approach. This is where smart manufacturing comes in. It combines intelligent chip design with sustainable production practices. Semiconductor equipment engineers and machine builders play a crucial role by collaborating to create a cohesive system that minimizes environmental impact while maximizing productivity.
The path to sustainability is smart manufacturing enabled, where the secure and sustainable design-to-production process for semiconductors becomes a Digital Enterprise (DE). DE serves as a comprehensive roadmap, a digital transformation pathway that guides semiconductor companies on their journey toward digital maturity and operational excellence.
As a digital enterprise, smart manufacturing capabilities, techniques and programs enable semiconductor manufacturers to achieve transformation by developing and executing one sustainable business strategy, from design to production to finished chip.
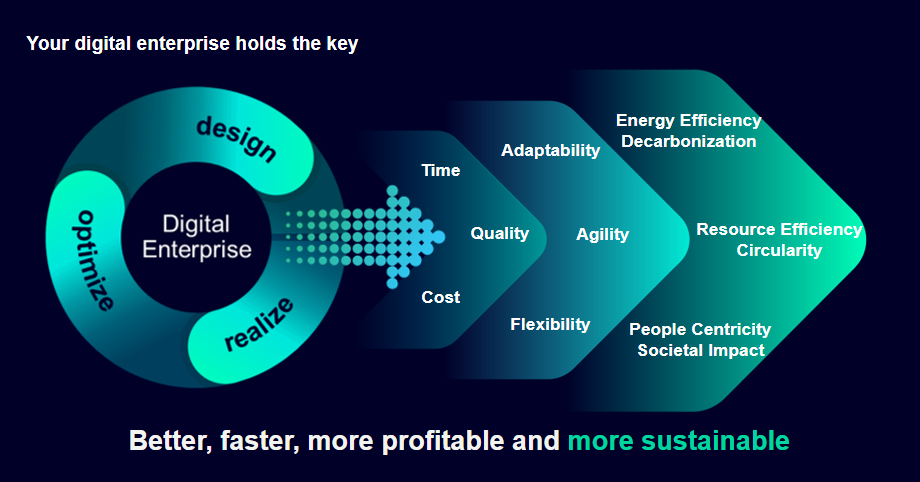
Embracing artificial intelligence (AI) and the advanced analytics of smart manufacturing provides semiconductor companies with real-time visibility into their production processes. Improved visibility enables optimized resource allocation and proactive identification of potential bottlenecks without disrupting operations. Pursuing a digital approach fosters agile, seamless operations, minimizes waste, and aligns progress with environmental responsibility.
Smart manufacturing makes the difference
With smart manufacturing, chipmakers and machine builders can design and build future-proof semiconductor fabs by implementing a wide range of digitally integrated automation solutions, reducing energy consumption, enhancing efficiency and productivity, and providing people-centric workspaces in plant operations.
Digitalization enables lifecycle management capabilities that connect every aspect of semiconductor manufacturing processes to establish a flexible plant where all product information and design data (customer requirements, original technical specifications, design definitions, production schedules, analysis results, sourcing plans, sustainability KPIs and quality inspections) are tied to critical processes and tasks all the way from requirements to final delivered chip. For complete traceability, compliance, and verification.

Semiconductors are the driving force behind modern automation, enabling data transparency and process optimization, ultimately leading us to a more sustainable future. This inter-dependency creates a virtuous feedback loop where chips activate smarter manufacturing practices, empower informed decisions, optimize resource utilization, and reduce the environmental footprint.
Simulation without interruption
Through collective intelligence, chipmakers can incorporate Digital Twins for highly accurate virtual models of the product, production, or production performance. Our Digital Twins enable a higher level of learning and advanced planning of fabs and machines, enabling an optimal system and energy setup. Yet it is important to remember that optimization should never interrupt production. Why?
Semiconductor companies face intense pressure to design and produce the next-generation chips while maintaining uninterrupted operations, which creates a ‘high-stakes environment’ where any disruption can have significant consequences.
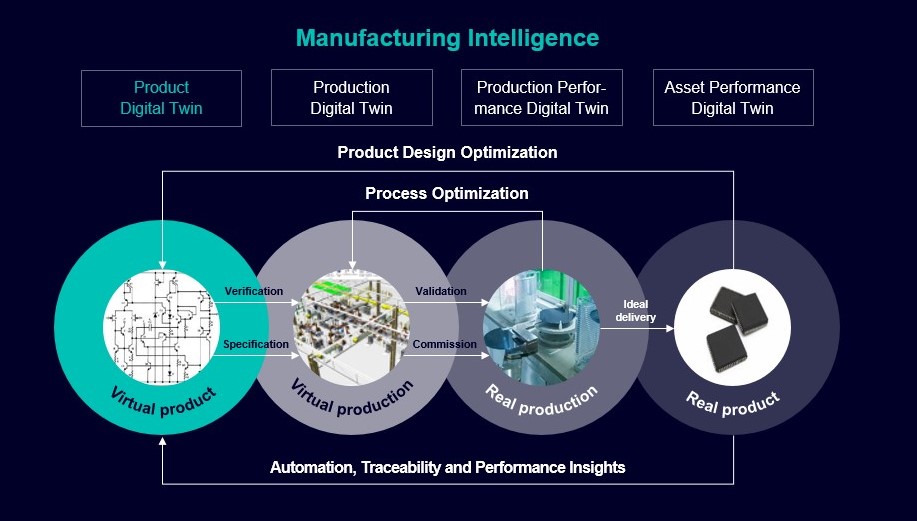
Fortunately, Siemens Digital Twin models can operate without disrupting any current operations, accurately simulating real-world conditions, while being continuously updated by real-time product and production data for a virtual model that is unparalleled for process optimization prior to building a semiconductor product, designing actual manufacturing operations, or planning equipment optimization.
A deeper understanding
Simulation with Digital Twins can enable multiple what-if scenarios that can be evaluated virtually at reduced cost to optimize products and processes. This comprehensive, real-time simulation of scenarios, processes, and systems fosters a deep understanding of plant dynamics that facilitates proactive problem-solving, predictive maintenance, and continuous improvement initiatives.
Cross domain Digital Twins can inform each other for insights and continuous improvement. As a result, Siemens smart solutions empower a synergy of Digital Twins with IoT and cutting-edge software and hardware tools that enable seamless integration, for next-generation efficiency in manufacturing operations and machine building that puts comprehensive sustainability goals within reach.
As a digital enterprise, smart manufacturing capabilities equip semiconductor manufacturers and machine builders to develop and execute a sustainable business strategy, from design to production to finished chip and beyond.
Very smart. But just as important, sustainable.
To discover more, take a look at our informative Sustainability Infographic:
Can’t view the file above? No worries, click here to view the Sustainability infographic.
Want to learn more about sustainability and semiconductors?
- Continue reading our blog series: Topic 2, Scale up smart to reduce carbon.
- View all the blogs in this series and read the topics that interest you most.
- Visit our exciting Hannover Messe digital experience to see our interactive showroom and listen to our recorded sessions.


