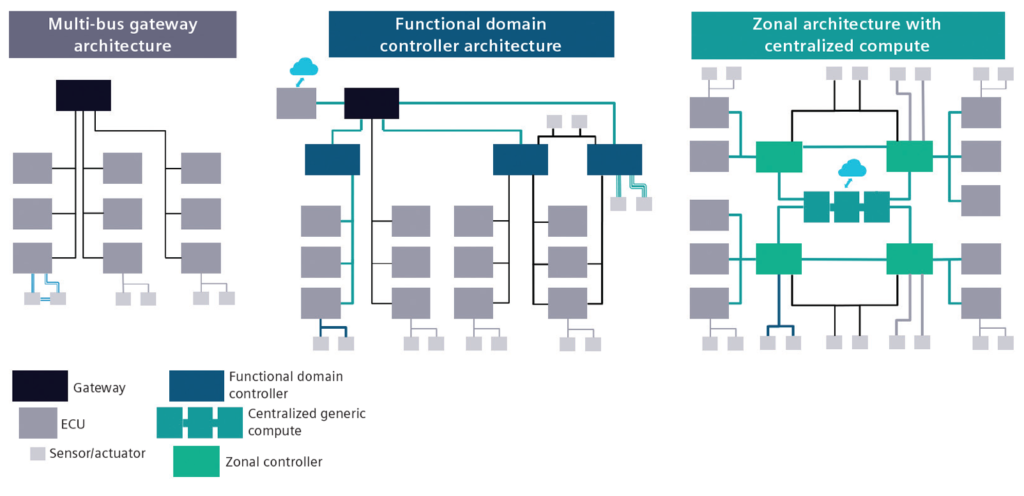
The evolution of E/E architecture in heavy equipment

As E/E architecture in heavy equipment evolves, electrical/electronic (E/E) architecture designs have become essential for meeting growing demands for efficiency, sustainability and resilience. As the heavy equipment industry experiences rapid change, manufacturers are under pressure to innovate.

In the eBook Key trends in E/E architecture for heavy equipment & off-road vehicles, you can explore in-depth the technologies and strategies driving smarter, safer and more efficient off-road vehicles. In this blog post, we explore 5 influential trends driving E/E architecture changes – from electrification to cybersecurity – and how they’re reshaping the industry.
1) Increased electrification
Driven by global environmental concerns and regulatory pressure to reduce carbon emissions, electrification is gaining traction in heavy equipment manufacturing. Governments worldwide are setting ambitious emissions reduction goals, such as the European Union’s target of cutting greenhouse gas emissions by at least 55% by 2030. These changes demand sustainable alternatives to traditional fossil fuels.
While advances in battery technology and electric powertrains have made electrification more feasible, reducing the total cost of ownership and increasing efficiency, electrification requires a complete rethinking of E/E architecture, especially in power distribution and management.
In this new model, traditional internal combustion engines must be replaced by high-voltage electric systems that require robust power electronics – inverters, converters and battery management systems, for example. Electric and hybrid powertrains need sophisticated control systems to balance power sources, energy usage and switching between electric and combustion modes.
The rise of electrified equipment has also brought about changes in thermal management and auxiliary systems, as batteries and motors generate substantial heat that must be managed efficiently to ensure longevity.
2) Enhanced machine control
Equipped with sensors such as LiDAR, radar and cameras, heavy machinery can now sense its environment with remarkable accuracy, enhancing safety and efficiency. AI algorithms process this data to make real-time decisions, performing tasks like route planning and obstacle detection autonomously.
This level of control requires complex E/E architecture to handle vast data flows from sensors and enable real-time processing. Autonomous systems boost productivity, since machines can operate continuously without fatigue. Still, manufacturers have to overcome an array of challenges, including sensor fusion, safety testing and navigating regulatory frameworks – and that often means that moving from basic automation to fully autonomous capabilities is an incremental process.
3) Advanced in-vehicle networks for connectivity
Advanced in-vehicle networks support data exchange between electronic control units (ECUs), sensors and actuators. This requires protocols such as Controller Area Network (CAN), J1939, and Ethernet to provide the communication backbone for real-time monitoring, diagnostics and control.
Adopting sophisticated network protocols such as these impacts E/E architecture by transforming communication from simple point-to-point connections to complex, hierarchical networks. With high-speed connectivity, these systems support data-intensive applications, enabling enhanced control strategies, predictive maintenance and scalability.
As connectivity improves, heavy equipment will become more capable of real-time diagnostics, improving operational efficiency and minimizing downtime.
4) IoT integration and connectivity
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing equipment operations by enabling real-time data exchange, predictive maintenance and fleet management. Cellular networks – 4G and 5G, satellite communication and Wi-Fi – enable IoT connectivity for equipment in diverse environments – even remote locations that lack cellular coverage.
With IoT, operators can monitor equipment remotely, optimize routes, schedule maintenance and address performance issues quickly, reducing downtime. For example, remote driving allows operators to control machinery from a distance, enhancing safety in hazardous or extreme environments.
As IoT adoption grows, operators can make data-driven decisions, enhancing equipment reliability and reducing operational costs.
5) Cybersecurity and E/E architecture in heavy equipment
Despite the benefits, the integration of IoT, ECUs and advanced networks also opens new cybersecurity challenges. Interconnected systems are vulnerable to attacks and the stakes are high: in 2023, the global average cost of a data breach reached $4.45 million. Cyber threats such as ransomware, unauthorized access and data breaches can compromise operational safety and lead to significant financial loss.
To protect E/E systems, manufacturers must prioritize cybersecurity. Best practices such as encryption, secure access controls and regular software updates can help, as can security audits, incident response plans and close collaboration with suppliers to ensure all components meet security standards.
Siemens solutions: Driving innovation in heavy equipment E/E architecture
Siemens offers a suite of solutions to help manufacturers navigate these trends in E/E architecture, including cloud based and software as a service tools for advanced electrification, IoT integration, machine control, and cybersecurity. Our technology empowers OEMs to streamline E/E architecture, enhance operational efficiency and ensure system security.
Download our eBook, Key Trends in E/E architecture for heavy equipment & off-road vehicles to learn more about the trends we touch on in this blog post and how Siemens’ supply chain solutions can help your organization stay ahead in the evolving heavy equipment market.
Related resources
Check out the following links for more information:
ONDEMAND WEBINAR: Maximize machine uptimes with smart electrical service documentation
WHITE PAPER: ECAD MCAD design process helps eliminate electromechanical issues
ONDEMAND WEBINAR: Network design software for E/E systems