What is the battery industry?
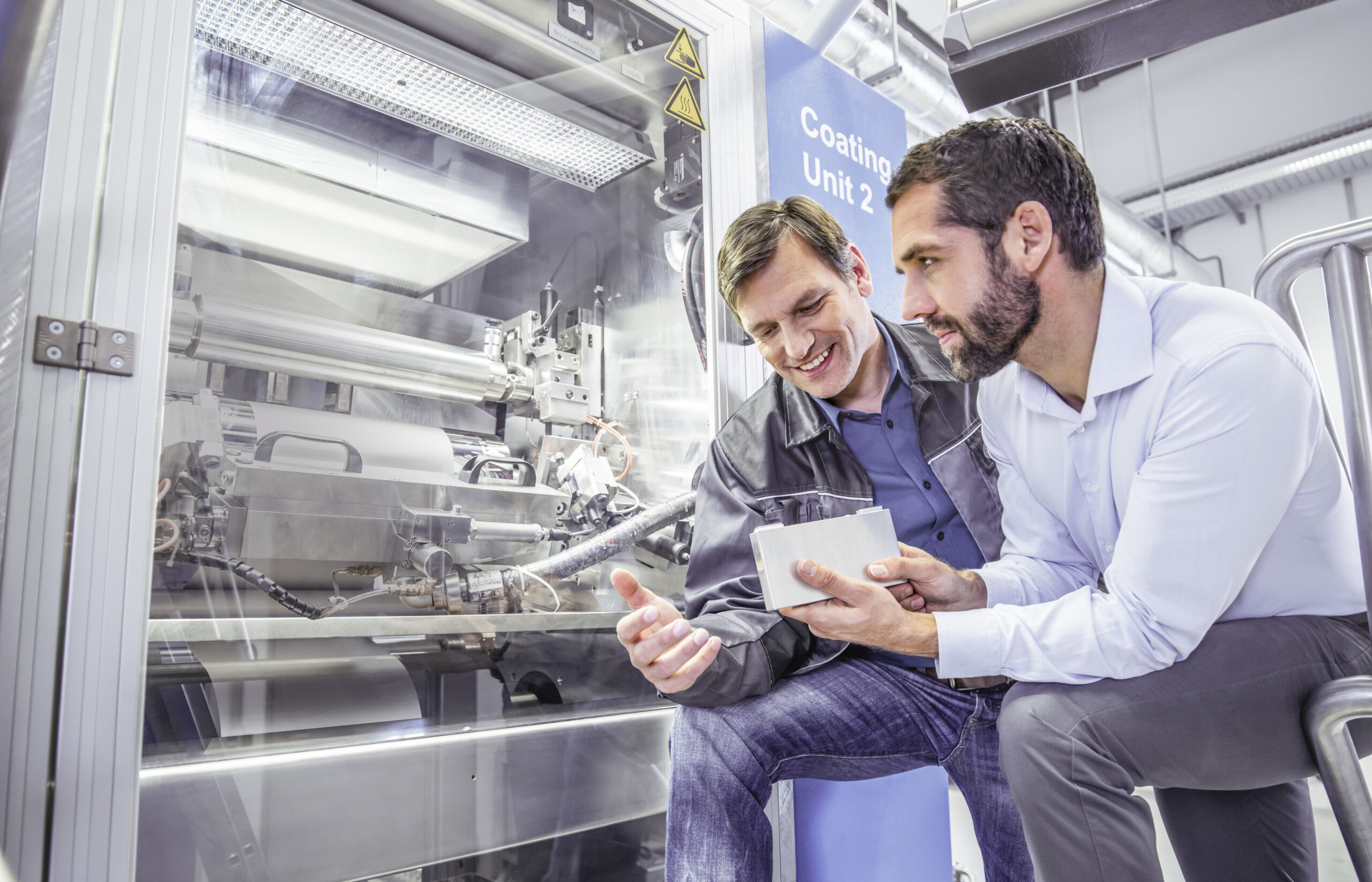

To match the growth of the battery industry globally, Siemens has launched The Battery Podcast a new series dedicated to discussions surrounding batteries. The first episode is already live, where you will get a background on our two hosts – Puneet Sinha and Marc Deyda – as well as some discussion as to why the battery industry will see so much change in the coming years. For the full discussion, I would highly recommend listening to episode one but you can continue reading here for some of the highlights from the episode.
Defining the battery industry
The first, and perhaps most important, part of the discussion was defining what we mean at Siemens when we talk about the battery industry. We are looking at the whole ecosystem from lithium mining and processing to material and chemistry development to cell and pack manufacturing, the integration of these batteries in systems (be it an electric car, electric aircraft, residential or grid level energy storage system) as well as recycling. It is important to look at the whole lifecycle because there are strong dependences, technology wise as well as the evolution of business, across all these partners and players.
Cell suppliers are increasingly looking to offer complete pack solutions. A lot of automotive OEMs as well as OEMs in other industries, such as aerospace and energy storage are heavily looking to morph themselves into battery businesses. They’re investing heavily in cell development and manufacturing. But there are also existing cell suppliers that are investing into new chemistries which will need to be rapidly scaled to industrial levels.
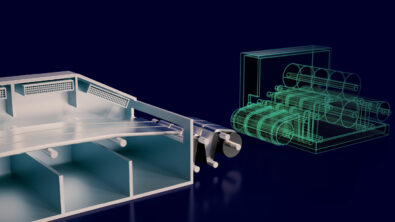
What is the gigafactory?
There are a lot of applications for batteries all around us and they all need to be fed with battery capacity. Not just one battery, but thousands and millions of batteries – this is the reason for the term gigafactory. It is also a measure of the battery capacity being manufactured, often described in gigawatt-hours. And as technologies improve and new chemistries come along, these huge factories need to scale to meet the demand of the market.
When a gigawatt-hour of manufacturing capacity can occupy as much as 10,000 square meters it is important to optimize the processes as much as possible. A 40 gigawatt-hour facility might manufacture 20 million cells a day, feeding 200,000 electric cars. That is only a fraction of what will be needed to hit global demand for electric only vehicles in parts of the world by 2030. And this is only one of the industries being supplied, there is also personal and grid storage for homes, the growing number of consumer electronics, and the many transportation systems looking to electrify with battery technologies in the coming decade.
How are we helping?
As a supplier we want to integrate the hardware, software, and services to create an accessible ecosystem for safe, rapid, and reliable battery development. It starts with planning the production processes – defining how much capacity is needed and start developing the factory in the virtual environment, aka the digital twin. That way you can measure throughput, energy efficiency, and even calculate the number of machines that will be needed to meet those requirements.
Next, we are helping businesses develop these highly customized machines with the machine builder. We are helping to integrate and standardize processes for greater potential with digitalization over time. Whether it is a new recipe or one being perfected, developing these processes in the digital environment with simulation tools provides greater optimization while reducing the risks associated with physical testing. It may also help with reorganizing the shop floor to minimize travel distances or improve flexibility should maintenance be required on one machine.
On top of all of the more traditional factory optimizations, we are also helping companies deploy artificial intelligence to improve process phases. One example is to use AI in defining the formation time of the battery cells. This can be a lengthy process and using the prediction afforded by AI it can be cut down as a massive benefit to manufacturers.
More to come
This conversation was the first of many and our hosts hope to talk to many people within the battery industry at every level. We also hope to tackle many of the different problems, drivers, and techniques throughout the industry as it rapidly develops globally. For more information today, you may want to check out the topic page siemens.com/battery. And Siemens will be attending many pf the premiere battery showcases in the coming months. Thank you and we hope to have you back soon for the next installment of The Battery Podcast.
Siemens Digital Industries (DI) is a leading innovator in automation and digitalization. In close cooperation with its partners and customers, DI is the driving force for the digital transformation in the process and manufacturing industries. With its Digital Enterprise portfolio, Siemens provides companies of all sizes with all the necessary products, along with consistent solutions and services for the integration and digitalization of the entire value chain. Optimized for the specific requirements of individual industries, this unique portfolio enables customers to enhance their productivity and flexibility. DI continuously extends its portfolio to include innovations and the integration of future-oriented technologies. Siemens Digital Industries, with its headquarters in Nuremberg, has a workforce of around 72,000 people worldwide.
For more information on Siemens Digital Industries products and services, follow us on LinkedIn, Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube.