Discover what’s new in Tecnomatix 2512 (December 2025)

Digitalization for advanced manufacturing.
The Tecnomatix® portfolio delivers advanced digital manufacturing software to empower businesses across diverse industries and sizes. Tecnomatix 2512 launched recently with several exciting new advancements in the areas of cloud computing, AI-driven technologies, collaboration, robotics simulation and offline programming human simulation and virtual reality.
In this blog, we explore how the Siemens Xcelerator portfolio, including Tecnomatix digital manufacturing software, helps companies minimize manufacturing risks and improve their production operations. Siemens Xcelerator is an open digital business platform that enables customers to accelerate their digital transformation easier, faster and at scale.
We are excited to bring these latest enhancements to you.
You don’t have Tecnomatix software?
See the highlights from Tecnomatix 2512:
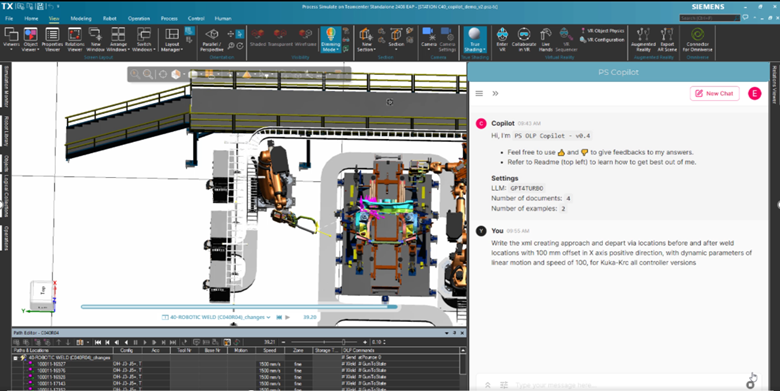
Process Simulate copilot
The Process Simulate copilot is your onboard AI assistant that provides instant insights and guidance by analyzing simulation and study data, with no training period required. In 2512 you can expect benefits of cloud-based deployment, artificial intelligence (AI) advancements, and new value-based licensing manufacturers gain the flexibility and security they need to scale their operations efficiently. The new value-based licensing provides a cost-effective solution with the ultimate flexibility.
Manufacturing teams can tap into the vast array of capabilities, whether you need them daily or occasionally. Teams can access a shared token pool to use advanced capabilities on demand, including VR Analysis, Automatic Path Planner, Cables, Roller Hemming, ARC Welding, Bin Picking, Pick & Place, and Simulation Copilot. Tokens are checked out only while tools are in use and returned when finished, enabling teams to run exactly what they need, when they need it—without fixed or per-seat licenses.
Prompt templates support a wide range of automated tasks, such as listing robots, selecting operations, running collision detection, and optimizing sequences, all via natural language prompts. Simulation agents automate compliance checks (study checker), cycle-time analysis (sequence optimizer), and operation creation, allowing your engineers to focus on innovation while reducing manual effort.
Advanced property-based object search enables precise queries and visual feedback for object properties, streamlining workflows and enhancing efficiency.
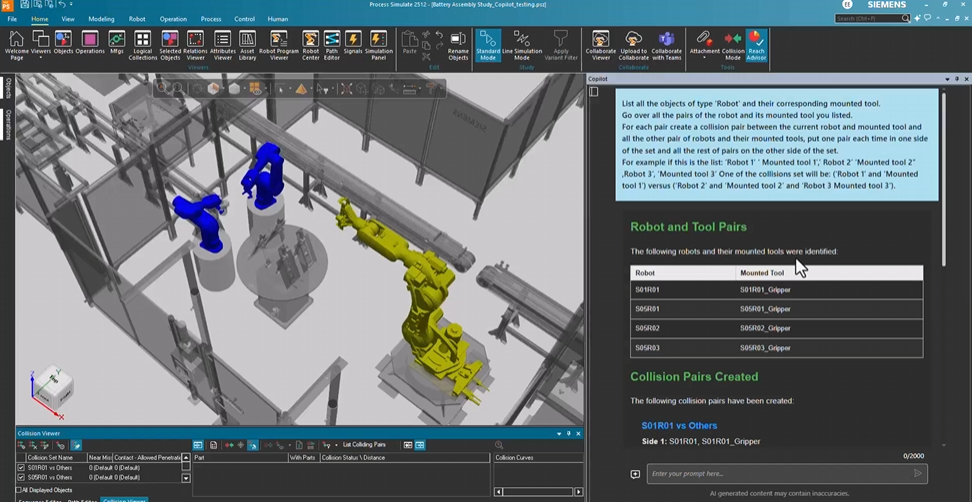
New capabilities for Process Simulate Copilot include:
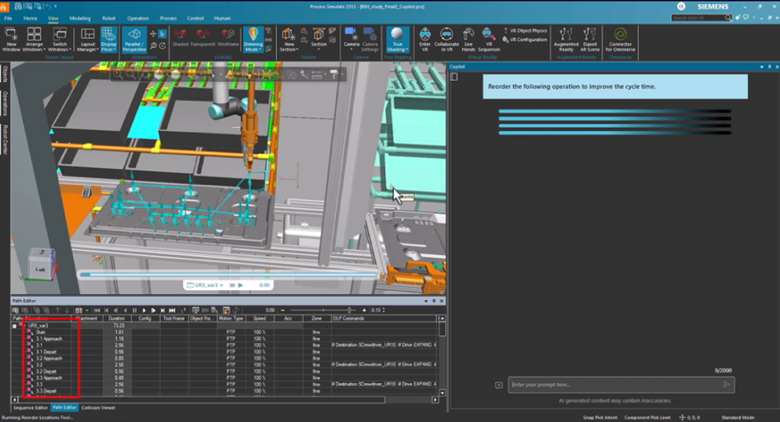
Sequence Optimizer
AI-driven analysis that identifies cycle-time bottlenecks and recommends targeted improvements, reducing manual effort while increasing throughput and planning efficiency.
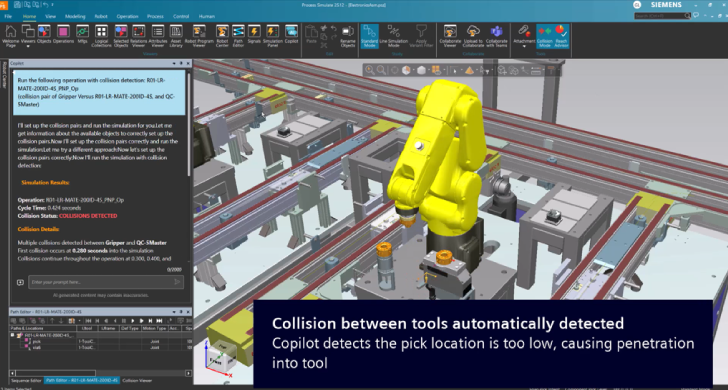
Operation Creation Assistant
Automates creation of optimized, collision-free robotic operations by detecting instructions, collisions, and bottlenecks, saving time, reducing errors, and improving consistency.
Queries by Server Properties
Enables precise, property-based searches and actions using a dedicated Copilot agent, with instant visual results for faster, more accurate object identification and automation.
General enhancements
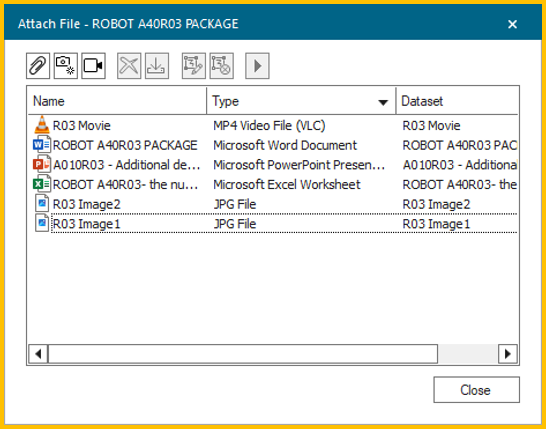
Enhanced file attachment capabilities
The attach file dialog has a new, unified interface for managing external files. You now can add, download, delete, and drag-and-drop files directly within Process Simulate, both in Teamcenter connected and standalone modes. All file changes are saved to the server and accessible to other Teamcenter applications, improving documentation and collaboration.
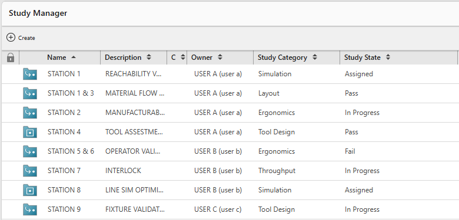
Study manager improvements
Studies now have “category” (simulation, ergonomics, layout, tool design, throughput) and “status” (assigned, in progress, pass, fail) fields managed via BMIDE.
These properties help planners and engineers organize, search, and update studies more efficiently, streamlining collaboration, teamwork and workflows.
Engineers can merge study scenes directly in Process Simulate, with expanded coverage for snapshots, user folders, and local components, reducing the need to switch to Teamcenter Manufacturing Process Planner (MPP).
Studies can be linked to specific projects, with access controlled by project membership, enhancing security and collaboration in multi-user environments.
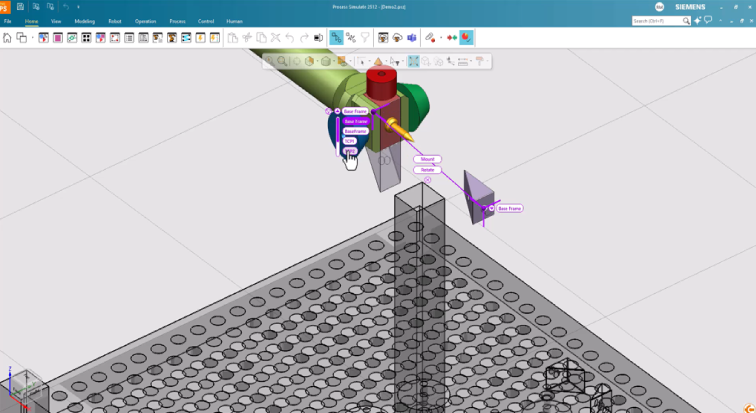
Rapid layout tool
The new rapid layout tool unifies the fast placement, mount, and unmount commands for easier layout creation. This allows rapid 2D placement and visual mounting of robotic tools directly in the graphic viewer, with intuitive controls for switching modes and previewing actions.
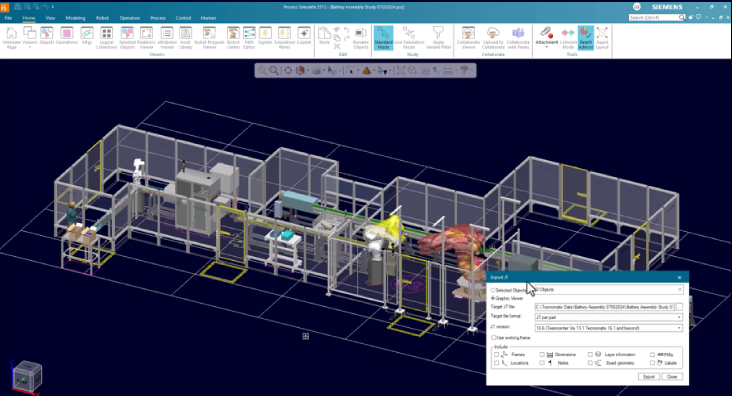
Export JT improvements
You now can export multiple objects and 3D volumes in a single JT export, with new API methods for custom export functions. Selected objects are highlighted and listed, improving feedback and reducing unnecessary work.
Process Simulate Collaborate
Tecnomatix Process Simulate Collaborate is a cloud-based, 3D simulation collaboration solution to visualize, review and analyze Process Simulate studies. It helps save time and effort by extending Process Simulate studies into the cloud, providing internal and external stakeholders access to the richness of your Process Simulate studies, saving time and effort. The Tecnomatix 2512 release introduces several innovative capabilities in Process Simulate Collaborate that enhance collaboration and efficiency in engineering workflows.
Advanced ergonomics
Using the advanced ergonomics capability, even deeper analytics are possible for manual workplaces.
As before, you can upload a picture of a worker in a certain position and convert that into a posture of a human model. It is now possible to conduct REBA analysis on that model, and if there are any problems with specific joints, they are highlighted directly in the 3D graphics, giving you even more intuitive access to the functionality.
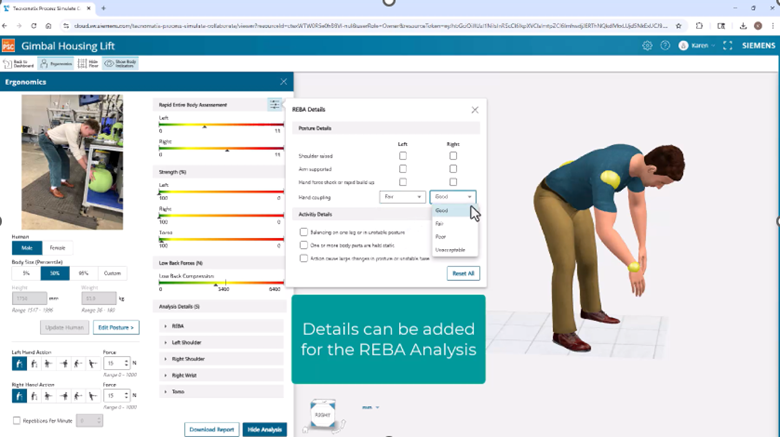
A complete report of the ergonomics results now can be downloaded as tabular data (.csv file).
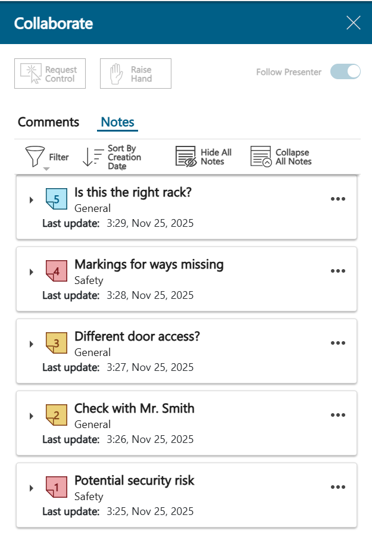
Notes usability enhancements
The Notes list in Process Simulate Collaborate has been improved to give quicker access to notes.
The first line of text in a note is now treated as the title in the notes list. This helps you quickly understand the content of a note without having to expand all the notes.
The ability to sort the list according to different properties (last update, type, priority, title, placement, location and creation date) has been added. This allows you to find the relevant notes for their current task much faster, i.e., to find the most critical notes or the ones with the most recent changes.
Advanced simulation controls
The usability of dimensions has been improved. Dimensions visibility has been greatly improved and study dimensions are now merged consistently.
The visibility of a dimension now takes into consideration the visibility of connected objects, so that when blanking certain areas for a better view the dimensions also follow suit. (The visibility of a dimension is now aligned with the visibility of its linked objects.)

Dimensions that exist in the study when the study is uploaded to Process Simulate Collaborate are now consistently merged and transferred also when the study is reuploaded.
Robotics and offline programming
Process Simulate Robotics helps you program and validate your robotic processes in a dynamic 3D environment. It includes robotics applications for spot welding, metal processing, drilling and riveting, surface treatment, and assembly.
The following new capabilities were released in Tecnomatix 2512.
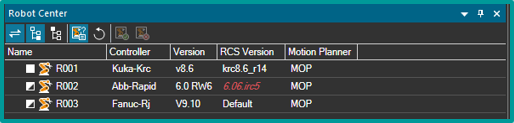
Robot center
Designed over the past two years, the robot center is a central viewer to control and visualize all aspects of robots within a study. This tool replaces legacy interfaces, streamlining robot setup, controller settings, and robot properties. The robot center aims to shorten the learning curve, improve discoverability, and consolidate robot-related commands, making it a game changer for both new and experienced users. Legacy tools such as robot setup, controller settings and robot properties will eventually be retired, with robot center now the recommended interface.
Continuous operations framework
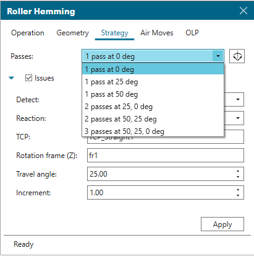
The new continuous operations framework allows you to set the intent for robotic paths, with locations generated as a byproduct. This approach enables flexible process path creation, built-in issue detection (such as collision, reach and singularity) and easy editing.
While setting the operation, users get a preview that shows the expected path. You can generate the path and have it placed in the path editor ready to simulate. The operation dialog remains open, allowing you to fine-tune the settings and apply again until you are happy with the path.
The operation is editable, so at any time it can be opened, adjusted as needed and reapplied. Operations can be copied, pasted, and adjusted, with plans for a template library to further streamline engineering workflows.
Roller hemming application
A dedicated application for roller hemming has been released with 2512, enabling you to select geometry, optimize reach and define multi-pass operations. The new roller hemming tool type allows for easy configuration of passes and angles, with instant simulation and editing capabilities.
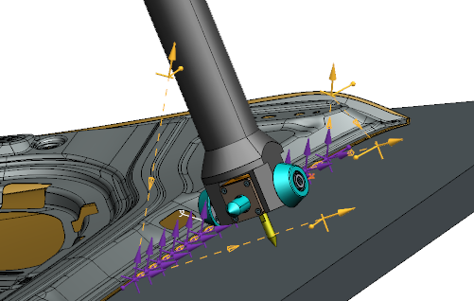
This dedicated capability provides a one-stop workflow where users select geometry edges, tools, and hemming angles, while the system automatically generates optimized multi-pass paths with reach optimization, air moves, and OLP support. With a single Apply action, a complete robotic path is created and ready for simulation, and users can edit and reapply the operation at any time to reflect updated conditions.
Arc weld trace and application
Arc welding simulation now dynamically visualizes (traces) weld seam creation, supporting various controllers and allowing you to control bead color and radius. The new arc welding application simplifies path creation, editing, and simulation, with advanced features planned for future releases (e.g., skip weld, multi-passes, weaving path, touch sense and external axis control). By addressing all aspects of the welding path in one place, the application streamlines optimization, improves accuracy, and supports more efficient engineering workflows.
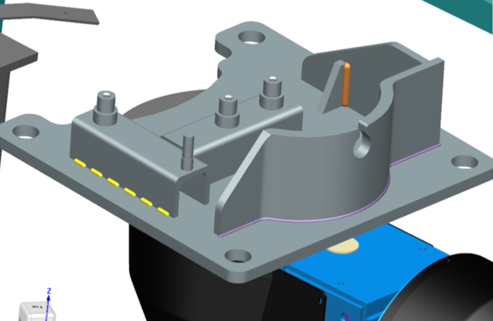
Material handling application
The new material handling application provides an intuitive interface for creating pick and place and bin-picking programs. It focuses on defining the intent of actions rather than manual path creation, with features like auto-generate, preview, and built-in air moves for enhanced usability.
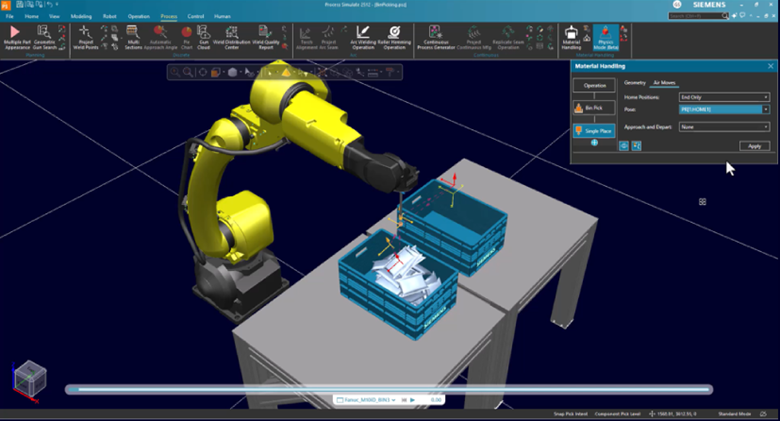
This dedicated, one-stop environment enables users to conceptualize, plan, optimize, and validate Pick & Place and Bin Picking applications by defining the intent of actions rather than manually creating locations and paths. With automatic previews, built-in air moves, and intuitive editing, users can quickly generate, simulate, and refine programs using a consistent workflow. The result is a more efficient offline programming experience that supports rapid setup, easier optimization, and faster validation of material handling operations.
Automatic path planner
You can now restrict motion along external axes for better control during path planning, improving maintainability and cycle time.
Brown-field optimization helps you to optimize existing operations for cycle time while preserving the overall motion shape and configuration of the operation.
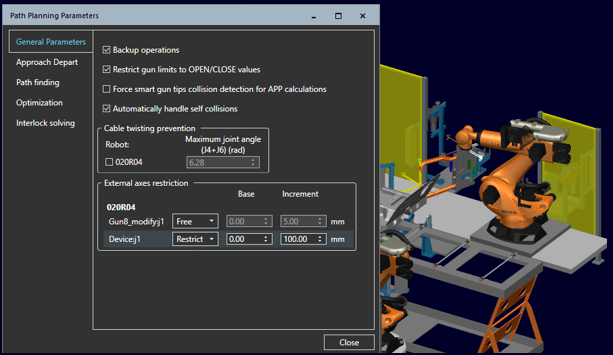
Robotic operations can now be assigned priorities to be used during interlock solving to reflect manufacturing constraints. This allows for better control and reduced cycle time in multi-robot environments whereby higher priority operations do not wait for lower priority operation progress and ensures that robots stop as late as possible and for the shortest possible time.
Human simulation and virtual reality
Process Simulate Human helps you to eliminate any risk to operators with walk path analysis, reachability tests, vision analysis and ergonomics assessments.
Process Simulate Virtual Reality delivers an immersive environment for better engineering reviews, staff training and realistic process validation.
The following new capabilities were released in Tecnomatix 2512.
Flexible cable simulation
Rigid cable geometry can now be transformed into flexible components, allowing for more realistic simulation of manual assembly and packaging. New features include the ability to add clips for physical anchoring, convert multi-segment cables, and fix end fittings for accurate simulation of cable bundles.
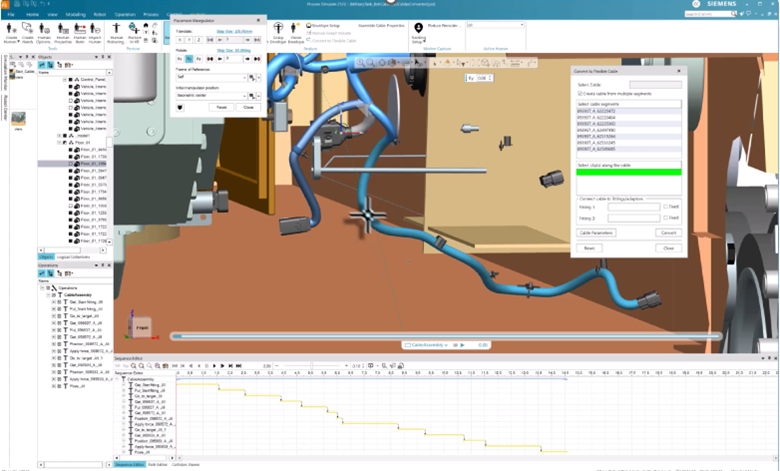
TSB flexible cables simulations
The task simulation builder (TSB) now enables humans to grasp, move, and assemble flexible cable elements, providing accurate insights into cable assembly processes and human performance demands such as posture and force. While flexible cable conversion focuses on creating physically realistic flexible cable models, TSB Flexible Cable Simulation builds on that foundation by enabling realistic human interaction with those cables during assembly tasks. As cables are manipulated, fastened sections remain fixed while free segments remain flexible, delivering accurate insight into routing feasibility, posture requirements, and force demands during manual assembly.
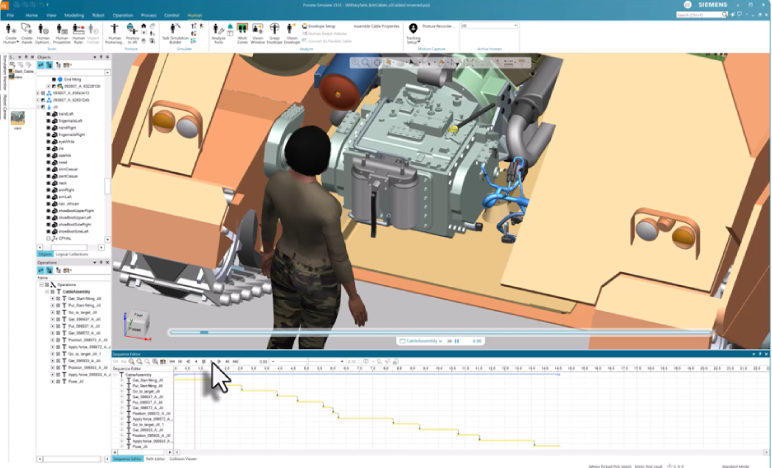
Improved grapsing
Improve realism and efficiency in human operation simulations with enhanced hand grasping. Precision and full-hand grasping have been reworked to better match real-world hand postures, reducing the need for manual adjustment. For precision grasps, users simply select a point to align the thumb pad, and the hand closes naturally while maintaining contact. For full-hand grasps, aligning the center of the palm automatically produces a realistic grip. These improvements deliver more accurate hand behavior, faster setup, and more consistent results when simulating manual tasks.

Clothing customizations
Human models can now be dressed in specialized clothing suitable for healthcare, industrial, defense, or casual environments, adding realism to simulations. Increase physical and contextual realism in human simulations with industry-specific clothing customization in 2512. Applying appropriate clothing improves visual fidelity and contextual accuracy, supporting more credible evaluation of human operations and clearer communication of simulation results to stakeholders.

Disembodied hands
New configurable disembodied hands (with or without forearms) and customizable skin tones allow for realistic hand representation and assessment of wrist posture and clearance. Improve hand-level analysis and clearance evaluation with new isolated hand models. Users can now create configurable hand models as hand-only or with a forearm, enabling more accurate assessment of wrist posture and forearm clearance during manual assembly tasks. With customizable skin tones and improved realism, these isolated hand models support clearer visualization, more precise ergonomic evaluation, and greater flexibility when planning and validating human operations.

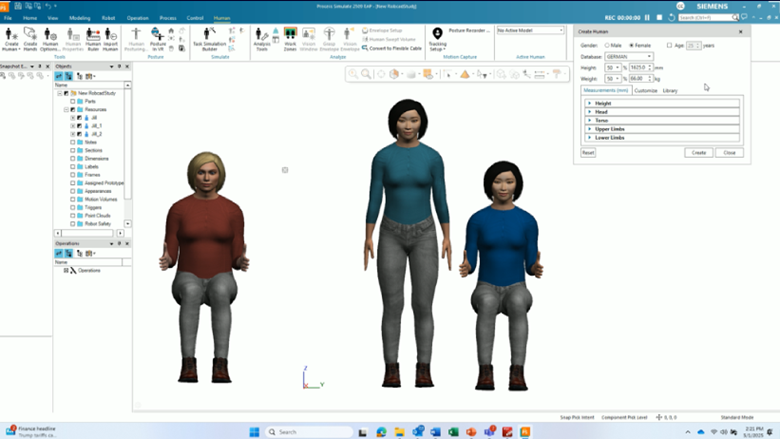
Flexible anthropometric scaling
The human scaling dialog supports a broader range of input combinations, enabling the creation of custom human models for specific assessment criteria, such as seated activities. The updated Human Scaling dialog now supports a broader range of scaling input combinations, enabling manufacturing engineers and ergonomists to create custom human models tailored to specific assessment criteria. This is especially beneficial when evaluating seated or posture-dependent tasks, where multiple anthropometric measurements taken in the working posture can be applied directly. The result is more realistic human models, more reliable ergonomic assessments, and better-informed workstation and process design decisions.
Time analysis using MTMmotion
MTMmotion® is a specialized approach for analyzing workplace activities. It can be used to generate detailed MTM-UAS time studies from TSB. For the 2512 release, this has been expanded to include the MTM-1 and Ergonomic Assessment Worksheet (EAWS) standards, automating industry-accepted time studies for process planning.
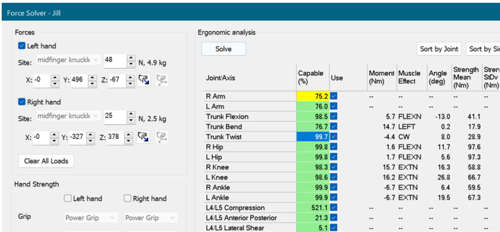
Strength assessment
The force solver tool now includes the arm force field strength model and the maximum acceptable effort (MAE) equation, providing more accurate estimates of human strength capabilities for ergonomic analysis. This release integrates the Arm Force Field strength model and the Maximum Acceptable Effort (MAE) equation, providing state-of-the-art prediction of manual arm strength, especially for repetitive tasks. By considering human anthropometry, posture, task frequency, low-back loading, and population-based strength data, the enhanced Force Solver delivers more reliable estimates of safe hand forces—supporting better ergonomic evaluation, safer workstation design, and improved protection of today’s workforce.
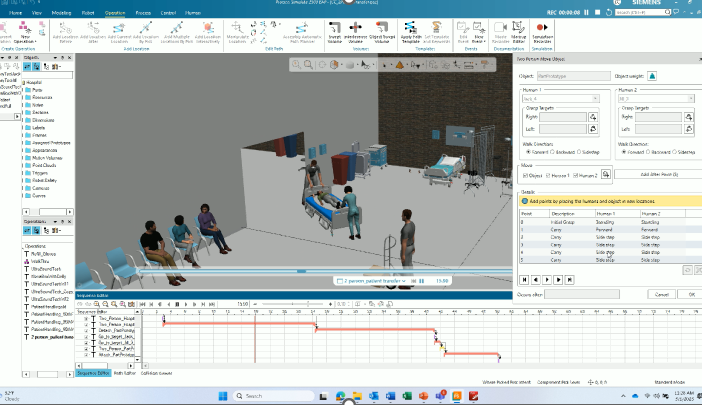
Two-person task simulation
TSB has been expanded to simulate tasks performed by two operators, supporting ergonomic analysis and accurate consideration of object weights in collaborative scenarios.
Meta Quest 3 headset support
Whole body tracking is now possible using the Quest 3 headset with six HTC VIVE trackers, offering flexibility in hardware configuration and enhanced realism during VR simulations. This flexible hardware configuration delivers highly realistic human movement in virtual environments, making it easier for manufacturing engineers and ergonomists to evaluate tasks, postures, and interactions with an unprecedented level of realism.

These are just highlights of the advancements delivered with the latest Tecnomatix release. For complete details on the new features of Tecnomatix 2512 and its supporting releases, please refer to the release notes and new features presentations offered with the software download.
Do not forget to join the Tecnomatix public community and to explore our website for even more exciting developments in digital manufacturing.

![Reshaping the world with digital manufacturing [VIDEO]](https://blogs.sw.siemens.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/7/2024/07/Zvi_2024_2-395x222.png)
