Advanced Nonlinear Memory Management
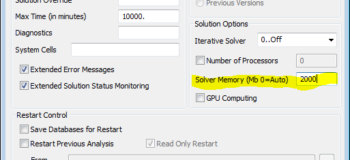
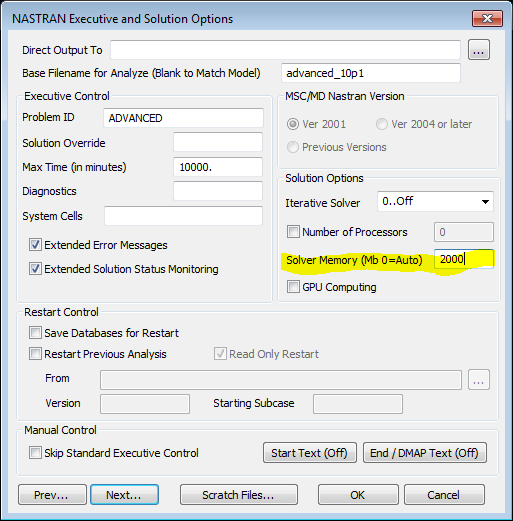
For users of SOL 601 Advanced Nonlinear, especially with large models, you might want to try the following settings to more efficiently allocate main memory for the solver.
The reason SOL601 requires some different settings is because Nastran actually spawns a second process for the advanced nonlinear solver. The primary Nastran job really only processes the input and then spawns the 601 solver which has its own memory allocation.
The default situation when running from Femap(or Nastran command line), is that the Nastran memory setting is passed to the 601 solver. If you increase this setting in Femap or on the Nastran command line, then Nastran and also the spawned SOL 601 process both get the same memory request(double dipping). This is really a waste of resource since the primary process only needs enough memory to read and process the input stream. It also means that using this method, you can never give SOL 601 more than half of your available main memory.
So, the desired situation is to make a “small” memory allocation for the primary Nastran process, leaving the remainder of your RAM memory available for the 601 solver.
The workaround for this is to use the windows env variable NXNA_MEMORY which specifies the sol 601 memory directly.
The most efficient setup would be to set NXNA_MEMORY to a “big” number and then inside Femap(or Nastran command line), set Nastran memory to a “small” number.
For example, on a machine with 32GB of RAM, you could try something like:
Femap memory=2000mb and set windows environment variable nxna_memory=26000mb

Stay tuned for the 11.3 release of Femap where we will introduce some additional, and easier ways to control the allocation of advanced nonlinear resources.


