Article Roundup: The ABCs of Functional Verification, Where are we with HDAP LVS verification?, Reducing Power at the RTL Level, An Optimal Path to DFT Automation, Embedded World 2020
- The ABCs of functional verification techniques
- Where are we with HDAP LVS verification?
- Reducing Power At The RTL Level
- An Optimal Path To DFT Automation
- Embedded World 2020
The ABCs of functional verification techniques
EEWorld
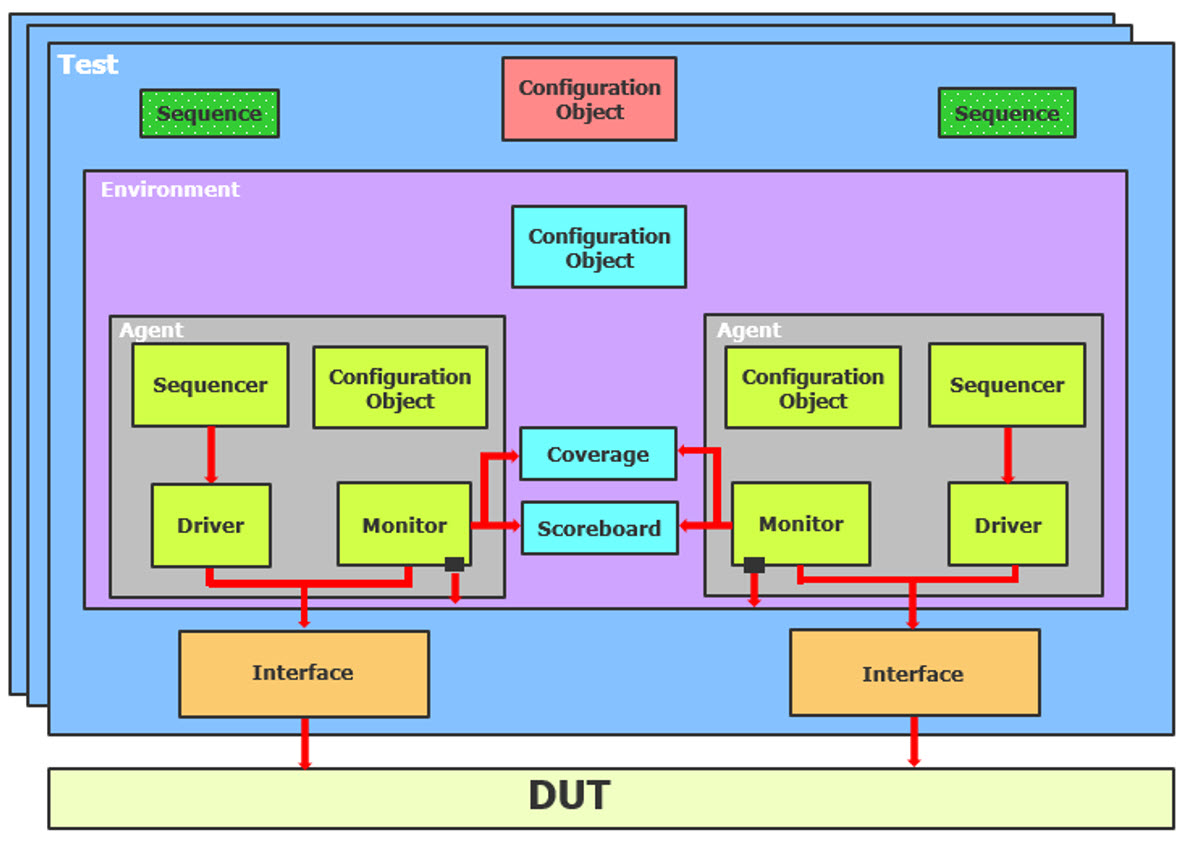 Functional verification helps demonstrate the functional correctness of a design and is one of the more challenges in the IC design cycle. In this article, FV is branched out into four types of techniques, namely: Static Verification, Functional Simulation, FPGA prototyping, Emulation and Universal Verification Methodology (UVM). This article highlights the purposes, advantages and limitations of these functional verification techniques and how Mentor’s platforms helps verify SoC designs by combining high-performance and high-capacity simulation with unified advanced debug and functional coverage capabilities.
Functional verification helps demonstrate the functional correctness of a design and is one of the more challenges in the IC design cycle. In this article, FV is branched out into four types of techniques, namely: Static Verification, Functional Simulation, FPGA prototyping, Emulation and Universal Verification Methodology (UVM). This article highlights the purposes, advantages and limitations of these functional verification techniques and how Mentor’s platforms helps verify SoC designs by combining high-performance and high-capacity simulation with unified advanced debug and functional coverage capabilities.
Where are we with HDAP LVS verification?
ChipScale
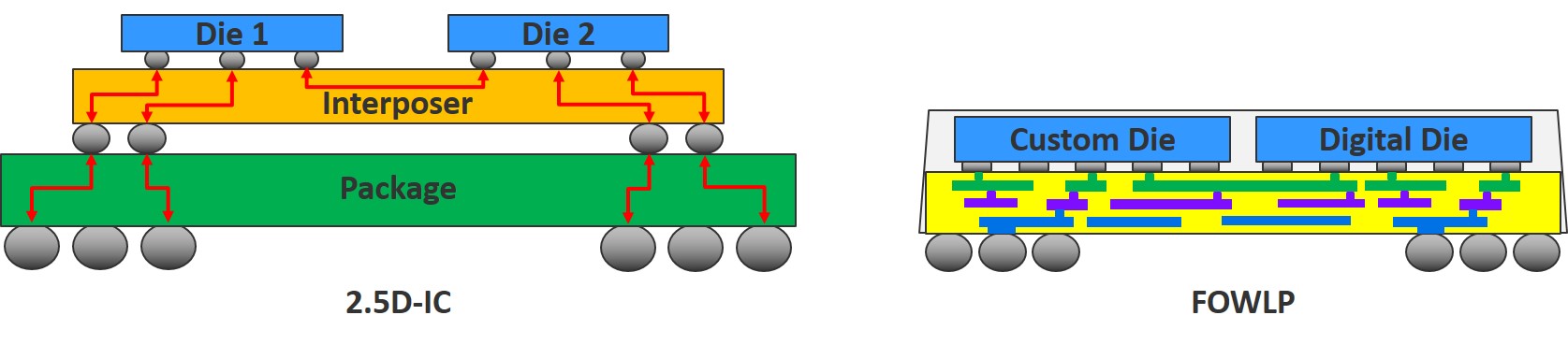 High Density packaging (HDAP) designs requires extensive verification to ensure they will perform as intended, and can be reliably manufactured in sufficient quantities to meet market demand. HDAP combines multiple IC dies in a single package. HDAP designs such as 2.5D interposer-based packages and fan-out wafer-level packages are driving a convergence between the traditional IC design and IC package design worlds. This article talks about the techniques to run full-package LVS verification, process ownership, the importance of package ADKs and more.
High Density packaging (HDAP) designs requires extensive verification to ensure they will perform as intended, and can be reliably manufactured in sufficient quantities to meet market demand. HDAP combines multiple IC dies in a single package. HDAP designs such as 2.5D interposer-based packages and fan-out wafer-level packages are driving a convergence between the traditional IC design and IC package design worlds. This article talks about the techniques to run full-package LVS verification, process ownership, the importance of package ADKs and more.
Reducing Power At The RTL Level
SemiEngineering
Power is a complex topic, and its implications in a design depends on a large number of variables. This article talks about RTL optimization, the unpredictable nature of power and implications during its reduction. By going with a manual flow, there is a high possibility of the designer to gain control over RTL. Automatic flow, provides a reduction of power, credibility of the RTL and its verification.
An Optimal Path To DFT Automation
SemiEngineering
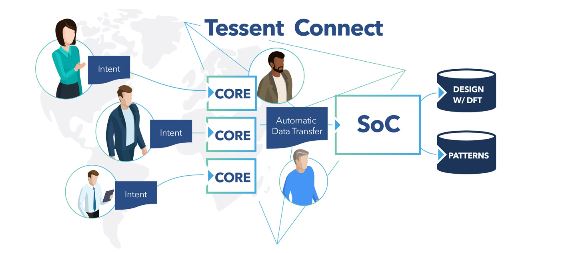 Hiererchical DFT uses existing hierarchy of a SoC to insert & generate test patterns at the core level. Taking the divide-and-conquer approach delivers real savings in test time and cost. This article talks about the challenges of adopting hierarchical DFT, different elements of end-to-end DFT automation & how it helps to keep DFT out of the critical path.
Hiererchical DFT uses existing hierarchy of a SoC to insert & generate test patterns at the core level. Taking the divide-and-conquer approach delivers real savings in test time and cost. This article talks about the challenges of adopting hierarchical DFT, different elements of end-to-end DFT automation & how it helps to keep DFT out of the critical path.
Embedded World 2020
MentorBlogs
 An embedded system has intrinsic intelligence that facilitates the possibility of predicting failure and mitigating its effects. The use of multiple operating systems on heterogeneous multicore devices will be explored, and how this facilitates the design of systems with multiple time domains – basically real-time and non-real-time components. Additionally, the concept of mixed criticality will be introduced – a design approach for systems where safety and certifiability are key requirements. This blog details Mentor’s plans for Embedded World 2020 and throws emphasis on each session & conference.
An embedded system has intrinsic intelligence that facilitates the possibility of predicting failure and mitigating its effects. The use of multiple operating systems on heterogeneous multicore devices will be explored, and how this facilitates the design of systems with multiple time domains – basically real-time and non-real-time components. Additionally, the concept of mixed criticality will be introduced – a design approach for systems where safety and certifiability are key requirements. This blog details Mentor’s plans for Embedded World 2020 and throws emphasis on each session & conference.