Discover design and manufacturing errors before the shop floor with a PCB digital twin
The least expensive time to catch manufacturing errors is not on the shop floor. Using a PCB digital twin, manufacturers can catch these errors earlier in the design process. Fixing these errors earlier is easier and more cost-effective to make changes. So, what’s a digital twin and how can it help us with manufacturing challenges today?
What is a PCB digital twin?
As described in this blog post, a digital twin is a virtual model of both the product and production process. Digital twins enable processes to be simulated and corrected before implementation on the shop floor. Better designs make it more likely that the first batch will be exactly right.
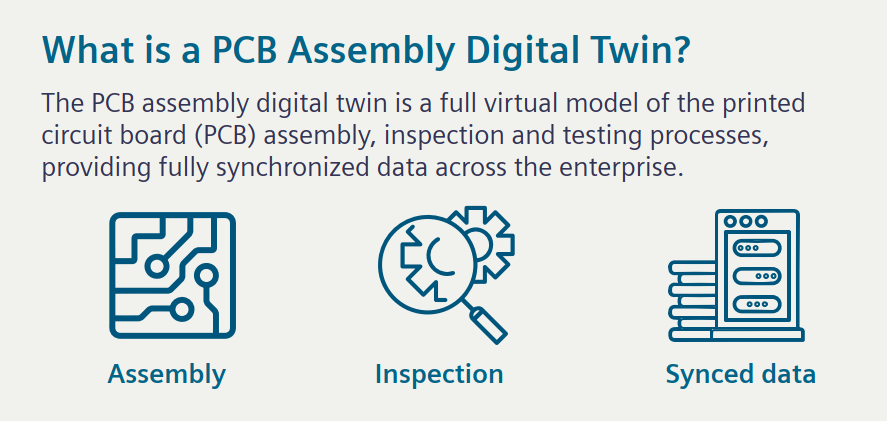
This infographic explains that the PCB assembly digital twin is a comprehensive virtual model of the printed circuit board assembly, inspection, and testing processes. It provides fully synchronized data across the enterprise.
Why now? Four challenges driving the need for PCB digital twins
Flexibility is the central theme for electronics manufacturer success today. Manufacturers need to be flexible in product customization and manufacturing production. But they also need to adapt to new market demands and encouraging traditionally separated teams to collaborate throughout the design process.
These challenges are driving the need for PCB digital twins:
- Decreased batch sizes: Increases in production customization leads to reduced lot sizes. Smaller project sizes raise the importance of accuracy and first-time-right boards to maintain profitability.
- Disconnected mechanical and electrical domains: Mechanical design changes often don’t consider electronics characteristics and vice versa. Shifting to a single unified data set shared between the domains is critical to overcoming challenges with increasingly complex designs.
- Supply chain disruptions requiring manufacturing flexibility: These disruptions challenge product vendors to quickly shift their operations from region to region. Global production agility involves digitalizing manufacturing processes for easy migration among vendors, each with its own production lines and machinery setup.
- Siloed testing and inspection machinery: Time-consuming and error-prone manual transfer of critical information from system to system. Since most testing and inspection machines include proprietary software, manufacturers must manage these self-contained silos.
Learn more about improving production yields, increasing profitability, and reducing errors on the production line by using a comprehensive digital twin to provide fully synchronized data across the enterprise.


