Article Roundup: 59% Power Savings for HPC Chip, Semiconductor Market Maturity, More Nodes More Problems, Aerospace ECAD-MCAD Co-Design & Portable Stimulus’ New Dynamic Constraints
- Case study demonstrates 59% extra power savings for HPC
- Semiconductor, EDA Industries Maturing? Wally Disagrees
- More Nodes, New Problems
- Applying Multi-Discipline Collaboration (ECAD/MCAD) to Reduce Program Risk
- Making Declarative Modeling Modular: Portable Stimulus Introduces Dynamic Constraints
Case study demonstrates 59% extra power savings for HPC
Tech Design Forum
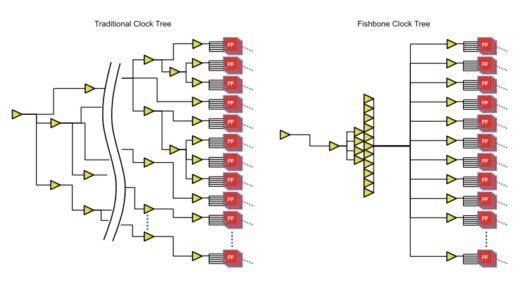 Taiwanese company Alchip achieved a 59% overall power reduction on a high-power computing (HPC) ASIC design using a unique clock design methodology and Mentor’s PowerPro RTL suite. Meanwhile, Alchip leveraged PowerPro’s automated sequential clock gating and optimized memory gating to reduce flip-flop power by 26% and memory power by 80%, contributing to the overall power savings. In addition, Alchip’s fishbone methodology reduced the number of clock buffer stages from 10-20 down to 2-3, resulting in a 10-25% savings of clock buffer area.
Taiwanese company Alchip achieved a 59% overall power reduction on a high-power computing (HPC) ASIC design using a unique clock design methodology and Mentor’s PowerPro RTL suite. Meanwhile, Alchip leveraged PowerPro’s automated sequential clock gating and optimized memory gating to reduce flip-flop power by 26% and memory power by 80%, contributing to the overall power savings. In addition, Alchip’s fishbone methodology reduced the number of clock buffer stages from 10-20 down to 2-3, resulting in a 10-25% savings of clock buffer area.
Semiconductor, EDA Industries Maturing? Wally Disagrees
SemiWiki
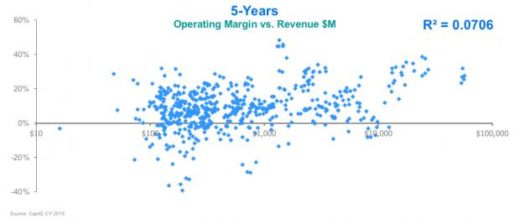 With the recent wave of acquisitions in the semiconductor industry, many experts perceived a maturing market that is consolidating. In contrast, Mentor’s CEO Wally Rhines says the acquisitions are not a sign of consolidation, but instead reflect specialization, as companies are focusing their investments in specific technology areas. The market is not maturing; rather it is evolving to meet new demands and applications.
With the recent wave of acquisitions in the semiconductor industry, many experts perceived a maturing market that is consolidating. In contrast, Mentor’s CEO Wally Rhines says the acquisitions are not a sign of consolidation, but instead reflect specialization, as companies are focusing their investments in specific technology areas. The market is not maturing; rather it is evolving to meet new demands and applications.
More Nodes, New Problems
SemiEngineering
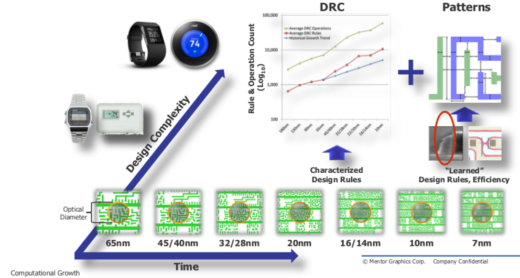 New leading-edge process nodes are rolling out at an accelerated pace despite rising costs and the increased difficulty of developing chips for these nodes. These new nodes introduce a host of new problems for chip design, verification, and more as the number of design rules explodes and the re-use of IP becomes less effective between nodes. One possible solution is the creation of heterogeneous chips that contain multiple process nodes on separate layers. But many of the problems remain the same, and experts are concerned that the pace at which new process nodes are being developed is unsustainable.
New leading-edge process nodes are rolling out at an accelerated pace despite rising costs and the increased difficulty of developing chips for these nodes. These new nodes introduce a host of new problems for chip design, verification, and more as the number of design rules explodes and the re-use of IP becomes less effective between nodes. One possible solution is the creation of heterogeneous chips that contain multiple process nodes on separate layers. But many of the problems remain the same, and experts are concerned that the pace at which new process nodes are being developed is unsustainable.
Applying Multi-Discipline Collaboration (ECAD/MCAD) to Reduce Program Risk
Air & Cosmos
 Modern aircraft design and manufacturing involves enormous complexity, risk, and cost as aircraft grow in sophistication both electrically and mechanically. In addition to increasing electro-mechanical design challenges, aircraft manufacturers must adhere to strict regulations, regarding the electrical wiring and interconnect systems (EWIS), that prevent cascading failures from harness chafing, arcing, and so forth. This article describes how an efficient and automated ECAD-MCAD co-design methodology is crucial for accurate design of these complicated systems while meeting strict guidelines and reducing project cost.
Modern aircraft design and manufacturing involves enormous complexity, risk, and cost as aircraft grow in sophistication both electrically and mechanically. In addition to increasing electro-mechanical design challenges, aircraft manufacturers must adhere to strict regulations, regarding the electrical wiring and interconnect systems (EWIS), that prevent cascading failures from harness chafing, arcing, and so forth. This article describes how an efficient and automated ECAD-MCAD co-design methodology is crucial for accurate design of these complicated systems while meeting strict guidelines and reducing project cost.
Making Declarative Modeling Modular: Portable Stimulus Introduces Dynamic Constraints
SemiEngineering
Accellera’s Portable Stimulus Standard supports advanced verification techniques such as object-oriented composition, constrained-random stimulus, and a new capability called dynamic constraints. Dynamic constraints streamline the process of creating highly portable test intent, and enable the capture of test intent at higher degrees of productivity and abstraction. This article examines several applications of this new capability along with examples to demonstrate how it can make test intent more flexible, modular, and reusable.
Comments
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Nice Article! And useful information you shared about 59% power saving for HPC chip, and also how an efficient and automated ECAD-MCAD co-design methodology is crucial for accurate design. Thanks for sharing.