Maximize diagnosis throughput with Dynamic Partitioning
Charged with the task of improving yield, product engineers need to find the location of defects in manufactured ICs quickly and efficiently.
Typically, product engineers use volume scan diagnosis to generate large amounts of data from failing test cycles. They can use this data to help choose failed devices for physical failure analysis, reduce the failure analysis time, find hidden systematic failures, and help direct design and manufacturing decisions that will ultimately improve yield.
However, performing volume scan diagnosis on today’s large, advanced node designs puts outsized demands on turn-around-time and compute resources. Now Mentor offers a new technology to maximize diagnosis throughput while performing ever more demanding scan diagnosis.
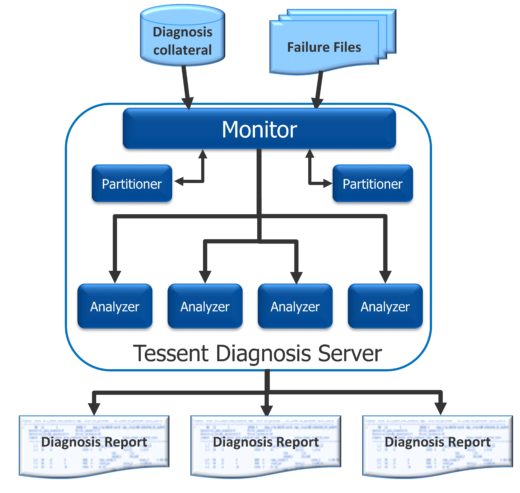
The technology, built into Tessent Diagnosis, is called dynamic partitioning. It works by first analyzing a fail log and then creating a partition that contains only the parts of the design that are relevant to that fail log. This partition serves as a new, smaller netlist that is used to perform the diagnosis.
Traditional volume scan diagnosis takes full design netlists as the input and requires many parallel simulation runs, but each run requires a similar memory resource. For a large design, you would need several large memory machines to perform parallel runs. You might have 20 machines, but only one is big enough to handle the job and the rest sit idle.
But what if you could reduce the design size? Dynamic partitioning does just that. Fail logs from the tester are analyzed by the Tessent Diagnosis Server, which works on your compute grid to both analyze and distribute the diagnosis processes. The server includes partitioners that create smaller files based on the fail logs, the analyzers that perform the actual diagnosis on the partitions, and a monitor that coordinates between the partitioners and analyzers and intelligently distributes the diagnosis processes.
Using the multiple smaller input files with just the relevant fail log data means that more processes (an unlimited number, actually) can be run in parallel, using a wider range of CPUs, and getting results faster and more efficiently than ever.
Dynamic partitioning was created to address hardware resource limitations by greatly reducing the memory footprint of the diagnosis process performed by the analyzers. Typically, the dynamic partitioning leads to a 5X reduction in memory and a runtime reduction of 50% per diagnosis report.
This dynamic partitioning technology makes a larger volume of scan diagnosis results available much faster, increasing the overall throughput of failure diagnosis by 10X. For existing Tessent Diagnosis users, setting up the dynamic partitioning flow is extremely easy. The benefits of dynamic partitioning include:
• Highly improved diagnosis throughput
• Reduced hardware resource requirements
• Enabler for volume diagnosis and yield analysis
Saving time and compute resources during volume scan diagnosis can confer a competitive advantage by reducing turn-around-time, equipment costs, and improving yield faster. Download our new whitepaper, Improve Volume Scan Diagnosis Throughput 10X with Dynamic Partitioning to learn more.