What is Design for Manufacturing?

Design for Manufacturing (DFM), also known as Design for Fabrication (DFF), is the engineering practice of designing products to facilitate the manufacturing process and reduce manufacturing costs. It means taking actual manufacturing capabilities into account when creating a product design and reviewing designs to ensure that they meet manufacturing specifications.
In principle, DFM can benefit any manufactured product, from the relatively small and simple, such as a wooden toy, to the largest and most sophisticated, such as electronic systems used for automotive and aerospace. In this article, we’re focusing on DFM in the electronic manufacturing process, and specifically on DFM for printed circuit boards – PCB DFM.
DFM is critical in the electronics industry. Electronics manufacturers must keep prices low in order to stay afloat in today’s competitive market, a demand that requires optimization of every aspect of production, including manufacturing. In addition, the fast pace of innovation in the electronics industry is driving companies to introduce new products at a dizzying pace. Without proper DFM, electronics manufacturers are forced to correct errors during pre-production manufacturing which creates significant delays and additional costs that no electronics manufacturer can afford.
What should be reviewed in PCB Design for Manufacturing (DFM?)
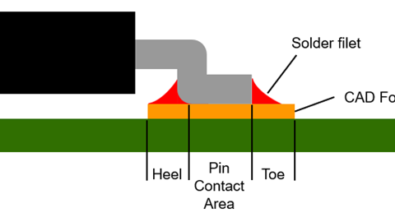
PCB DFM looks at all factors that may impact the manufacturability of a PCB design, such as assembly, fabrication, flex/rigid-flex, microvia, panel and substrate. It should also consider whether SMT component placement and soldering can be conducted automatically to reduce costs. DFM can involve general manufacturing specifications and/or the specifications of a specific manufacturer.
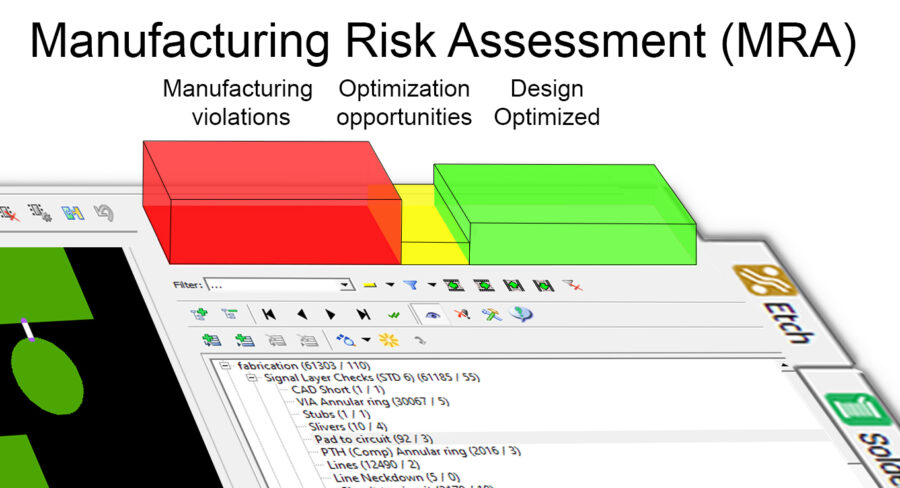
Given the complexity of the electronic manufacturing process, DFM principles are applied in specific ways to several key stages within the PCB design-to-manufacturing workflow, and even beyond it. This has given rise to several subsets of DFM, each of which focuses on optimizing different aspects of the manufacturing process.
Design for assembly (DFA) – Focuses on facilitating assembly operations, minimizing the number of parts, improving the ease of handling and using standardized parts to make assembly more efficient
Design for testing (DFT) – Incorporates features in the design that make it easier to test the product for defects that could impact its functioning
Design for excellence (DFX) – Implemented in the concept design phase; includes methods, guidelines, and standards for creating better-quality products
When should PCB DFM reviews be done?
DFM reviews can be conducted at various stages in the PCB design and manufacturing process, but as a general principle, the earlier, the better. Ideally, DFM reviews should be done during the design stage, especially when introducing a new product. This is known as shift-left. The timing is critical because the sooner a potential issue is identified, the less costly fixing it will be.
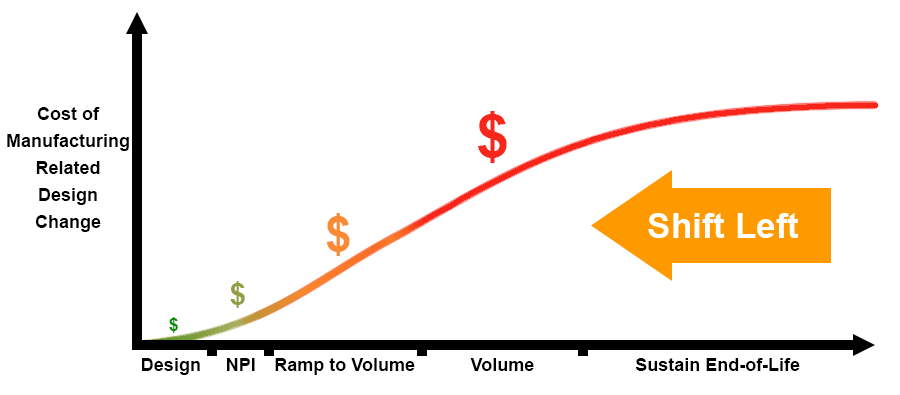
Reviewing the design for fabrication issues in the design stage enables designers to create a more mature design and catch errors and violations early on, before time and valuable materials have been wasted on a problematic design. Additionally, when a design is reviewed at an early stage, it can also be optimized for specific production volumes, including high mix, low volume production.
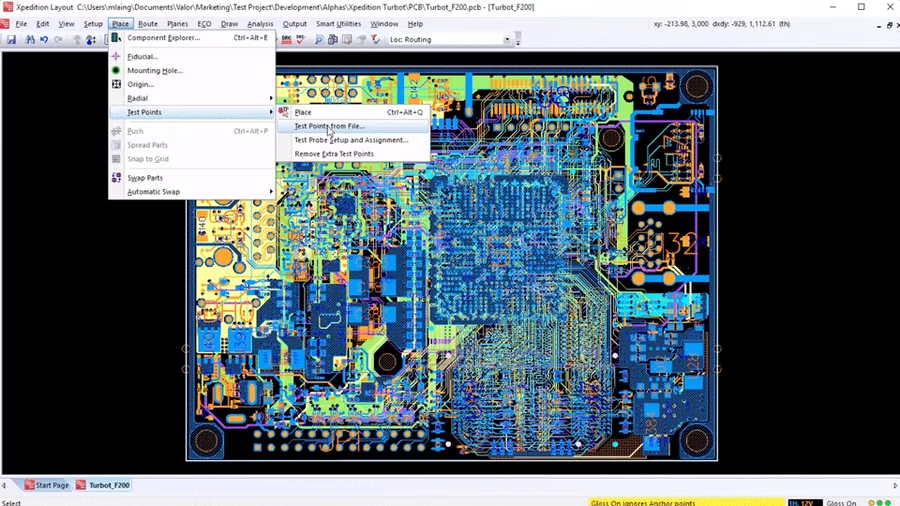
Accelerating new product introduction with Valor NPI
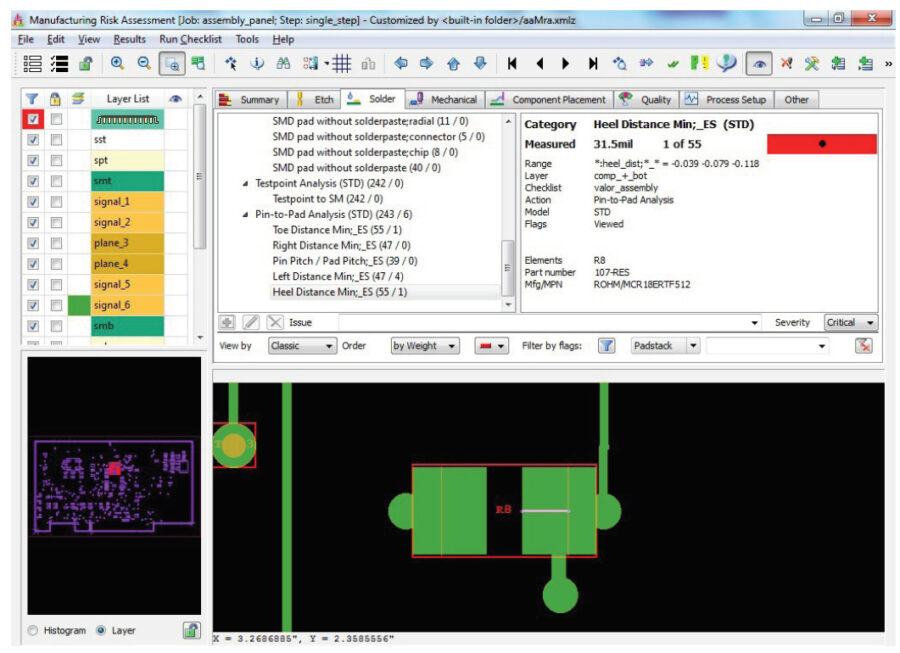
DFM is no longer a post-layout process in PCB design. It is now considered throughout the shift-left concurrent design flow. From test-point definition and validation to DFM analysis during layout, designers can eliminate errors before PCB assembly. DFM validation ensures a seamless and error free design-to-manufacturing hand-off.
Who should be involved in DFM?
DFM isn’t solely the responsibility of designers. Shift-left of DFM requires that all stakeholders, including engineers, designers, contract manufacturers, and material suppliers challenge the design and inspect it on every level to ensure that every element has been optimized and all unnecessary costs have been eliminated. A full DFM review can also determine if the board can be efficiently produced by a given manufacturer according to the manufacturer’s specific manufacturing capabilities and constraints.
Involving all stakeholders minimizes board spins and iterations, saving the tedious back and forth between designers and manufacturers, and accelerating the time to market and reducing costs. When all stakeholders review the design for reliability, assuring that the PCB will perform as expected for its projected lifetime, it helps to streamline the handoff between design and manufacturing and ensure that the manufacturing team receives complete PCB design data.
PCB DFM moves to the cloud
DFM can be a cumbersome process, as designs need to be sent back and forth between the designer and each manufacturer until all of the problems are corrected according to the specifications of that manufacturer. However, new advances that move many aspects of PCB DFM to the cloud have vastly simplified and sped up DFM reviews. Cloud-based DFM platforms enable designers and manufacturers to easily define custom DFM rules and safely share sensitive data in real-time, ensuring a smart and seamless handoff. They also allow designers to submit designs to several manufacturers and compare results before selecting a manufacturer.
PCB DFM—a critical component of a smart electronics manufacturing process
Innovation has accelerated the pace of electronics manufacturing exponentially and profit margins are smaller than ever before. Everything in the electronics manufacturing process must be optimized—there is simply no time for multiple late-stage iterations or for costly mistakes that waste time and material. DFM is a critical to speeding up the process and minimizing costs by optimizing the handoff between design and manufacturing and ensuring first-time-right PCB production.
Explore Valor NPI with our Online Trial
Explore Valor NPI with our free online trial and find out how easy it is to implement the world’s most advanced DFM software. With no download or installation necessary, this simple guided tour provides immediate hands-on experience. Select your desired workflow: